User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
Follow our continuing CROI coverage
Keep up to date with the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections home page for the latest in ID Practitioner's continuing reporting from the CROI meeting and our follow-ups afterward. You can also check out our archival coverage from last year's meeting.
Keep up to date with the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections home page for the latest in ID Practitioner's continuing reporting from the CROI meeting and our follow-ups afterward. You can also check out our archival coverage from last year's meeting.
Keep up to date with the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections home page for the latest in ID Practitioner's continuing reporting from the CROI meeting and our follow-ups afterward. You can also check out our archival coverage from last year's meeting.
Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167861</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FD43.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FD43</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240426T111340</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240426T114737</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240426T114737</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240426T114737</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Jennifer Nelson</byline> <bylineText>JENNIFER NELSON</bylineText> <bylineFull>JENNIFER NELSON</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The switch is the first of its kind in the United States and comes on the heels of a decision from 2021 by the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA) t</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>In June, Oregon PAs will be referred to as Physician Associates, a title change from Physician Assistants being debated nationwide. </teaser> <title>Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>5</term> <term>6</term> <term>15</term> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>9</term> <term>34</term> <term>13</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>52226</term> <term>22</term> <term>23</term> <term>31</term> <term>25</term> <term>26</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.aapa.org/news-central/2024/04/oregon-governor-tina-kotek-signs-law-changing-pa-title/?utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=aapa_post&utm_campaign=news_central">bill</a></span> into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state. <span class="tag metaDescription">The switch is the first of its kind in the United States and comes on the heels of a decision from 2021 by the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA) to change the meaning of “PA” to “physician associate” from “physician assistant.”</span></p> <p>In the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/slideshow/2023-physician-assistant-satisfaction-6016503#2">Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023</a>, </span>a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.<br/><br/>According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/985263">working independently</a></span> with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.<br/><br/>Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.<br/><br/>Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.<br/><br/>Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.<br/><br/>The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/oregon-physician-assistants-get-name-change-2024a100084h">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Automated Risk Assessment Tool Reduces Antibiotic Prescribing Rates
An algorithm-driven risk assessment embedded in an electronic health record (EHR) helped clinicians reduce inappropriate broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribing by 17.4% and 28.4% in patients with UTIs and pneumonia, respectively, according to two related studies published in JAMA.
The randomized control trials included more than 200,000 adult patients with non–life threatening pneumonia or urinary tract infections (UTIs) in 59 hospitals owned by HCA Healthcare across the country.
Researchers analyzed baseline prescribing behaviors over an 18-month period starting in April 2017, and data from a 15-month period of implementation of the new antibiotic system starting in April 2019.
, according to lead author Shruti K. Gohil, MD, MPH, associate medical director of epidemiology and infection prevention, infectious diseases at the University of California Irvine School of Medicine.
“When a patient comes in with pneumonia or a UTI, it’s precisely because we are concerned that our patients have a multidrug-resistant organism that we end up using broad-spectrum antibiotics,” she said.
Despite growing awareness of the need to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, clinicians have still been slow to adopt a more conservative approach to prescribing, Dr. Gohil said.
“What physicians have been needing is something to hang their hat on, to be able to say, ‘Okay, well, this one’s a low-risk person,’ ” Dr. Gohil said.
The trials compared the impact of routine antibiotic activities with a stewardship bundle, called INSPIRE (Intelligent Stewardship Prompts to Improve Real-time Empiric Antibiotic Selection).
Both groups received educational materials, quarterly coaching calls, prospective evaluations for antibiotic use, and were required to select a reason for prescribing an antibiotic.
But prescribers in the intervention group took part in monthly coaching calls and feedback reports. In addition, if a clinician ordered a broad-spectrum antibiotic to treat pneumonia or a UTI outside of the intensive care unit within 72 hours of admission, an EHR prompt would pop up. The pop-up suggested a standard-spectrum antibiotic instead if patient risk for developing a multidrug-resistant (MDRO) version of either condition was less than 10%.
An algorithm used data from the EHR calculated risk, using factors like patient demographics and history and MDRO infection at the community and hospital level.
Prescribing rates were based on the number of days a patient received a broad-spectrum antibiotic during the first 72 hours of hospitalization.
For the UTI intervention group, rates dropped by 17.4% (rate ratio [RR], 0.83; 95% CI, 0.77-0.89; P < .001), and 28.4% reduction in the pneumonia group (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.66-0.78; P < .001).
“We cannot know which element — prompt, education, or feedback — worked, but the data suggests that the prompt was the main driver,” Dr. Gohil said.
“In antibiotic stewardship, we have learned not only that doctors want to do the right thing, but that we as stewards need to make it easy for them do the right thing,” said Paul Pottinger, MD, professor of medicine at the Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The prompt “is your easy button,” said Dr. Pottinger, who was not involved with either study. “The researchers made it simple, fast, and straightforward, so people don’t have to think about it too much.”
The studies showed similar safety outcomes for the control and intervention groups. Among patients with a UTI, those in the control group were transferred to the ICU after an average of 6.6 days compared to 7 days in the intervention group. Among patients with pneumonia, the average days to ICU transfer were 6.5 for the control group and 7.1 for the intervention group.
“This study is a proof of concept that physicians want to do the right thing and are willing to trust this information,” Dr. Pottinger said. “And this also shows us that this tool can be refined and made even more precise over time.”
The study was funded by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and was led by the University of California Irvine, Harvard Pilgrim Healthcare Institute, and HCA Healthcare System. Various authors report funding and support from entities outside the submitted work. The full list can be found with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An algorithm-driven risk assessment embedded in an electronic health record (EHR) helped clinicians reduce inappropriate broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribing by 17.4% and 28.4% in patients with UTIs and pneumonia, respectively, according to two related studies published in JAMA.
The randomized control trials included more than 200,000 adult patients with non–life threatening pneumonia or urinary tract infections (UTIs) in 59 hospitals owned by HCA Healthcare across the country.
Researchers analyzed baseline prescribing behaviors over an 18-month period starting in April 2017, and data from a 15-month period of implementation of the new antibiotic system starting in April 2019.
, according to lead author Shruti K. Gohil, MD, MPH, associate medical director of epidemiology and infection prevention, infectious diseases at the University of California Irvine School of Medicine.
“When a patient comes in with pneumonia or a UTI, it’s precisely because we are concerned that our patients have a multidrug-resistant organism that we end up using broad-spectrum antibiotics,” she said.
Despite growing awareness of the need to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, clinicians have still been slow to adopt a more conservative approach to prescribing, Dr. Gohil said.
“What physicians have been needing is something to hang their hat on, to be able to say, ‘Okay, well, this one’s a low-risk person,’ ” Dr. Gohil said.
The trials compared the impact of routine antibiotic activities with a stewardship bundle, called INSPIRE (Intelligent Stewardship Prompts to Improve Real-time Empiric Antibiotic Selection).
Both groups received educational materials, quarterly coaching calls, prospective evaluations for antibiotic use, and were required to select a reason for prescribing an antibiotic.
But prescribers in the intervention group took part in monthly coaching calls and feedback reports. In addition, if a clinician ordered a broad-spectrum antibiotic to treat pneumonia or a UTI outside of the intensive care unit within 72 hours of admission, an EHR prompt would pop up. The pop-up suggested a standard-spectrum antibiotic instead if patient risk for developing a multidrug-resistant (MDRO) version of either condition was less than 10%.
An algorithm used data from the EHR calculated risk, using factors like patient demographics and history and MDRO infection at the community and hospital level.
Prescribing rates were based on the number of days a patient received a broad-spectrum antibiotic during the first 72 hours of hospitalization.
For the UTI intervention group, rates dropped by 17.4% (rate ratio [RR], 0.83; 95% CI, 0.77-0.89; P < .001), and 28.4% reduction in the pneumonia group (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.66-0.78; P < .001).
“We cannot know which element — prompt, education, or feedback — worked, but the data suggests that the prompt was the main driver,” Dr. Gohil said.
“In antibiotic stewardship, we have learned not only that doctors want to do the right thing, but that we as stewards need to make it easy for them do the right thing,” said Paul Pottinger, MD, professor of medicine at the Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The prompt “is your easy button,” said Dr. Pottinger, who was not involved with either study. “The researchers made it simple, fast, and straightforward, so people don’t have to think about it too much.”
The studies showed similar safety outcomes for the control and intervention groups. Among patients with a UTI, those in the control group were transferred to the ICU after an average of 6.6 days compared to 7 days in the intervention group. Among patients with pneumonia, the average days to ICU transfer were 6.5 for the control group and 7.1 for the intervention group.
“This study is a proof of concept that physicians want to do the right thing and are willing to trust this information,” Dr. Pottinger said. “And this also shows us that this tool can be refined and made even more precise over time.”
The study was funded by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and was led by the University of California Irvine, Harvard Pilgrim Healthcare Institute, and HCA Healthcare System. Various authors report funding and support from entities outside the submitted work. The full list can be found with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An algorithm-driven risk assessment embedded in an electronic health record (EHR) helped clinicians reduce inappropriate broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribing by 17.4% and 28.4% in patients with UTIs and pneumonia, respectively, according to two related studies published in JAMA.
The randomized control trials included more than 200,000 adult patients with non–life threatening pneumonia or urinary tract infections (UTIs) in 59 hospitals owned by HCA Healthcare across the country.
Researchers analyzed baseline prescribing behaviors over an 18-month period starting in April 2017, and data from a 15-month period of implementation of the new antibiotic system starting in April 2019.
, according to lead author Shruti K. Gohil, MD, MPH, associate medical director of epidemiology and infection prevention, infectious diseases at the University of California Irvine School of Medicine.
“When a patient comes in with pneumonia or a UTI, it’s precisely because we are concerned that our patients have a multidrug-resistant organism that we end up using broad-spectrum antibiotics,” she said.
Despite growing awareness of the need to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, clinicians have still been slow to adopt a more conservative approach to prescribing, Dr. Gohil said.
“What physicians have been needing is something to hang their hat on, to be able to say, ‘Okay, well, this one’s a low-risk person,’ ” Dr. Gohil said.
The trials compared the impact of routine antibiotic activities with a stewardship bundle, called INSPIRE (Intelligent Stewardship Prompts to Improve Real-time Empiric Antibiotic Selection).
Both groups received educational materials, quarterly coaching calls, prospective evaluations for antibiotic use, and were required to select a reason for prescribing an antibiotic.
But prescribers in the intervention group took part in monthly coaching calls and feedback reports. In addition, if a clinician ordered a broad-spectrum antibiotic to treat pneumonia or a UTI outside of the intensive care unit within 72 hours of admission, an EHR prompt would pop up. The pop-up suggested a standard-spectrum antibiotic instead if patient risk for developing a multidrug-resistant (MDRO) version of either condition was less than 10%.
An algorithm used data from the EHR calculated risk, using factors like patient demographics and history and MDRO infection at the community and hospital level.
Prescribing rates were based on the number of days a patient received a broad-spectrum antibiotic during the first 72 hours of hospitalization.
For the UTI intervention group, rates dropped by 17.4% (rate ratio [RR], 0.83; 95% CI, 0.77-0.89; P < .001), and 28.4% reduction in the pneumonia group (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.66-0.78; P < .001).
“We cannot know which element — prompt, education, or feedback — worked, but the data suggests that the prompt was the main driver,” Dr. Gohil said.
“In antibiotic stewardship, we have learned not only that doctors want to do the right thing, but that we as stewards need to make it easy for them do the right thing,” said Paul Pottinger, MD, professor of medicine at the Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The prompt “is your easy button,” said Dr. Pottinger, who was not involved with either study. “The researchers made it simple, fast, and straightforward, so people don’t have to think about it too much.”
The studies showed similar safety outcomes for the control and intervention groups. Among patients with a UTI, those in the control group were transferred to the ICU after an average of 6.6 days compared to 7 days in the intervention group. Among patients with pneumonia, the average days to ICU transfer were 6.5 for the control group and 7.1 for the intervention group.
“This study is a proof of concept that physicians want to do the right thing and are willing to trust this information,” Dr. Pottinger said. “And this also shows us that this tool can be refined and made even more precise over time.”
The study was funded by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and was led by the University of California Irvine, Harvard Pilgrim Healthcare Institute, and HCA Healthcare System. Various authors report funding and support from entities outside the submitted work. The full list can be found with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167858</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FD21.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FD21</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240425T180607</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240426T093431</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240426T093431</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240426T093431</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Brittany Vargas</byline> <bylineText>BRITTANY VARGAS</bylineText> <bylineFull>BRITTANY VARGAS</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>They focused on the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics during the first 3 days of hospital admission, before microbiologic test results came back, and when clini</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>An EHR-based risk assessment tool aided clinicians in not prescribing an unnecessary broad-spectrum antibiotic, study states.</teaser> <title>Automated Risk Assessment Tool Reduces Antibiotic Prescribing Rates</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>em</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>14</term> <term>15</term> <term>6</term> <term>23</term> <term>20</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">280</term> <term>284</term> <term>315</term> <term>50732</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Automated Risk Assessment Tool Reduces Antibiotic Prescribing Rates</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><br/><br/>An algorithm-driven risk assessment embedded in an electronic health record (EHR) helped clinicians reduce inappropriate broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribing by 17.4% and 28.4% in patients with UTIs and pneumonia, respectively, according to two related studies published in <em>JAMA</em>.<br/><br/>The randomized control trials included more than 200,000 adult patients with <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2817976?guestAccessKey=b3f1c55d-c178-42cb-a223-8933eba2fec1&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041924">non–life threatening pneumonia</a></span> or <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2817975">urinary tract infections (UTIs)</a></span> in 59 hospitals owned by HCA Healthcare across the country. <br/><br/>Researchers analyzed baseline prescribing behaviors over an 18-month period starting in April 2017, and data from a 15-month period of implementation of the new antibiotic system starting in April 2019.<br/><br/><span class="tag metaDescription">They focused on the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics during the first 3 days of hospital admission, before microbiologic test results came back, and when clinicians are likely to err on the side of caution and prescribe one of the drugs</span>, according to lead author Shruti K. Gohil, MD, MPH, associate medical director of epidemiology and infection prevention, infectious diseases at the University of California Irvine School of Medicine. <br/><br/>“When a patient comes in with pneumonia or a UTI, it’s precisely because we are concerned that our patients have a multidrug-resistant organism that we end up using broad-spectrum antibiotics,” she said. <br/><br/>Despite growing awareness of the need to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, clinicians have still been slow to adopt a more conservative approach to prescribing, Dr. Gohil said. <br/><br/>“What physicians have been needing is something to hang their hat on, to be able to say, ‘Okay, well, this one’s a low-risk person,’ ” Dr. Gohil said. <br/><br/>The trials compared the impact of routine antibiotic activities with a stewardship bundle, called INSPIRE (Intelligent Stewardship Prompts to Improve Real-time Empiric Antibiotic Selection). <br/><br/>Both groups received educational materials, quarterly coaching calls, prospective evaluations for antibiotic use, and were required to select a reason for prescribing an antibiotic. <br/><br/>But prescribers in the intervention group took part in monthly coaching calls and feedback reports. In addition, if a clinician ordered a broad-spectrum antibiotic to treat pneumonia or a UTI outside of the intensive care unit within 72 hours of admission, an EHR prompt would pop up. The pop-up suggested a standard-spectrum antibiotic instead if patient risk for developing a multidrug-resistant (MDRO) version of either condition was less than 10%. <br/><br/>An algorithm used data from the EHR calculated risk, using factors like patient demographics and history and MDRO infection at the community and hospital level. <br/><br/>Prescribing rates were based on the number of days a patient received a broad-spectrum antibiotic during the first 72 hours of hospitalization. <br/><br/>For the UTI intervention group, rates dropped by 17.4% (rate ratio [RR], 0.83; 95% CI, 0.77-0.89; <em>P</em> < .001), and 28.4% reduction in the pneumonia group (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.66-0.78; <em>P</em> < .001). <br/><br/>“We cannot know which element — prompt, education, or feedback — worked, but the data suggests that the prompt was the main driver,” Dr. Gohil said.<br/><br/>“In antibiotic stewardship, we have learned not only that doctors want to do the right thing, but that we as stewards need to make it easy for them do the right thing,” said Paul Pottinger, MD, professor of medicine at the Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle. <br/><br/>The prompt “is your easy button,” said Dr. Pottinger, who was not involved with either study. “The researchers made it simple, fast, and straightforward, so people don’t have to think about it too much.”<br/><br/>The studies showed similar safety outcomes for the control and intervention groups. Among patients with a UTI, those in the control group were transferred to the ICU after an average of 6.6 days compared to 7 days in the intervention group. Among patients with pneumonia, the average days to ICU transfer were 6.5 for the control group and 7.1 for the intervention group. <br/><br/>“This study is a proof of concept that physicians want to do the right thing and are willing to trust this information,” Dr. Pottinger said. “And this also shows us that this tool can be refined and made even more precise over time.” <br/><br/>The study was funded by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and was led by the University of California Irvine, Harvard Pilgrim Healthcare Institute, and HCA Healthcare System. Various authors report funding and support from entities outside the submitted work. The full list can be found with the original articles.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/automated-patient-risk-assessment-lowers-antibiotic-2024a1000801">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Hepatitis Kills 3500 People Each Day, Says WHO
The number of deaths from viral hepatitis worldwide increased from 1.1 million in 2019 to 1.3 million in 2022. These figures equate to approximately 3500 deaths per day due to the disease, which is the second leading cause of mortality from infectious agents globally.
These data are part of the recently released Global Hepatitis Report 2024, which was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) during the World Hepatitis Summit in Lisbon, Portugal.
“This report paints a concerning picture: Despite global progress in preventing hepatitis infections, deaths are increasing because very few people with hepatitis are being diagnosed and treated,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
Hepatitis B significantly is associated with the highest mortality rate. It accounted for 83% of deaths from the disease in 2022. Meanwhile, hepatitis C was responsible for 17% of deaths. The mortality of other, less common types of hepatitis was not considered in the ranking.
The report also indicates that more than 6000 people worldwide are infected with viral hepatitis every day. The 2.2 million new cases in 2022 represent a slight decrease from 2.5 million in 2019, but the WHO considers the incidence high.
The organization’s updated statistics indicate that about 254 million people had hepatitis B in 2022, while 50 million had type C.
“Besides the deaths, the number of new cases every year is also striking. These are diseases that continue to spread. In the case of hepatitis C, the spread results from lack of access to disposable or properly sterilized sharp materials,” said Thor Dantas, MD, PhD, a physician and director of the Brazilian Society of Hepatology’s Viral Hepatitis Committee.
The situation of hepatitis B is particularly problematic, given that there is a safe and effective vaccine against it, said Dantas. “It’s remarkable that we continue to have so many new cases worldwide. This shows that we are failing in access to preventive measures for control and spread.”
Half of chronic hepatitis B and C cases occur in people between ages 30 and 54 years, while 12% affect children. There are more infections among men, who represent 58% of all cases.
The WHO also drew attention to the difficulty of accessing diagnosis and treatment. Only 13% of people with chronic hepatitis B infection were diagnosed, while only 3% — equivalent to 7 million people — received antiviral therapy by the end of 2022. This result is well below the WHO’s global target, which aims to treat 80% of cases by 2030.
Brazil has a higher diagnostic rate than the global average but is still below the target. According to the report, in 2022, the country diagnosed 34.2% of all hepatitis B infections. However, treatment coverage remains low: 3.6% of the total.
For hepatitis C, the scenario is somewhat different. During the same period, Brazil diagnosed 36% of total cases, with a treatment rate of 24%.
In 2022, Brazil had 2578 deaths from hepatitis B and 2977 from hepatitis C.
Because hepatitis is a silent disease, diagnosis often comes late, when the disease is already quite advanced, said Dr. Dantas. “Viral hepatitis evolves over the years essentially asymptomatically. Malaria shows symptoms, and tuberculosis shows symptoms. Viral hepatitis does not. They are only discovered through active searching.”
The WHO report shows significant regional differences in infection rates. Almost two thirds of cases are concentrated in the following 10 countries: China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Russia.
In terms of hepatitis C incidence, Brazil ranks 15th globally, with 536,000 cases in 2022, representing 1.1% of the global total. The list is led by Pakistan, with 8.8 million cases, equivalent to 17.8% of the total. Next are India, with 5.5 million (11.2%), and China, with 4 million (8.1%).
In addition to regional differences, the report also reveals profound disparities in the prices paid for major treatments.
“Price disparities between, and even within, WHO regions persist, with many countries paying above global reference values, including for nonpatented medications,” according to the report.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of deaths from viral hepatitis worldwide increased from 1.1 million in 2019 to 1.3 million in 2022. These figures equate to approximately 3500 deaths per day due to the disease, which is the second leading cause of mortality from infectious agents globally.
These data are part of the recently released Global Hepatitis Report 2024, which was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) during the World Hepatitis Summit in Lisbon, Portugal.
“This report paints a concerning picture: Despite global progress in preventing hepatitis infections, deaths are increasing because very few people with hepatitis are being diagnosed and treated,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
Hepatitis B significantly is associated with the highest mortality rate. It accounted for 83% of deaths from the disease in 2022. Meanwhile, hepatitis C was responsible for 17% of deaths. The mortality of other, less common types of hepatitis was not considered in the ranking.
The report also indicates that more than 6000 people worldwide are infected with viral hepatitis every day. The 2.2 million new cases in 2022 represent a slight decrease from 2.5 million in 2019, but the WHO considers the incidence high.
The organization’s updated statistics indicate that about 254 million people had hepatitis B in 2022, while 50 million had type C.
“Besides the deaths, the number of new cases every year is also striking. These are diseases that continue to spread. In the case of hepatitis C, the spread results from lack of access to disposable or properly sterilized sharp materials,” said Thor Dantas, MD, PhD, a physician and director of the Brazilian Society of Hepatology’s Viral Hepatitis Committee.
The situation of hepatitis B is particularly problematic, given that there is a safe and effective vaccine against it, said Dantas. “It’s remarkable that we continue to have so many new cases worldwide. This shows that we are failing in access to preventive measures for control and spread.”
Half of chronic hepatitis B and C cases occur in people between ages 30 and 54 years, while 12% affect children. There are more infections among men, who represent 58% of all cases.
The WHO also drew attention to the difficulty of accessing diagnosis and treatment. Only 13% of people with chronic hepatitis B infection were diagnosed, while only 3% — equivalent to 7 million people — received antiviral therapy by the end of 2022. This result is well below the WHO’s global target, which aims to treat 80% of cases by 2030.
Brazil has a higher diagnostic rate than the global average but is still below the target. According to the report, in 2022, the country diagnosed 34.2% of all hepatitis B infections. However, treatment coverage remains low: 3.6% of the total.
For hepatitis C, the scenario is somewhat different. During the same period, Brazil diagnosed 36% of total cases, with a treatment rate of 24%.
In 2022, Brazil had 2578 deaths from hepatitis B and 2977 from hepatitis C.
Because hepatitis is a silent disease, diagnosis often comes late, when the disease is already quite advanced, said Dr. Dantas. “Viral hepatitis evolves over the years essentially asymptomatically. Malaria shows symptoms, and tuberculosis shows symptoms. Viral hepatitis does not. They are only discovered through active searching.”
The WHO report shows significant regional differences in infection rates. Almost two thirds of cases are concentrated in the following 10 countries: China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Russia.
In terms of hepatitis C incidence, Brazil ranks 15th globally, with 536,000 cases in 2022, representing 1.1% of the global total. The list is led by Pakistan, with 8.8 million cases, equivalent to 17.8% of the total. Next are India, with 5.5 million (11.2%), and China, with 4 million (8.1%).
In addition to regional differences, the report also reveals profound disparities in the prices paid for major treatments.
“Price disparities between, and even within, WHO regions persist, with many countries paying above global reference values, including for nonpatented medications,” according to the report.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of deaths from viral hepatitis worldwide increased from 1.1 million in 2019 to 1.3 million in 2022. These figures equate to approximately 3500 deaths per day due to the disease, which is the second leading cause of mortality from infectious agents globally.
These data are part of the recently released Global Hepatitis Report 2024, which was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) during the World Hepatitis Summit in Lisbon, Portugal.
“This report paints a concerning picture: Despite global progress in preventing hepatitis infections, deaths are increasing because very few people with hepatitis are being diagnosed and treated,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
Hepatitis B significantly is associated with the highest mortality rate. It accounted for 83% of deaths from the disease in 2022. Meanwhile, hepatitis C was responsible for 17% of deaths. The mortality of other, less common types of hepatitis was not considered in the ranking.
The report also indicates that more than 6000 people worldwide are infected with viral hepatitis every day. The 2.2 million new cases in 2022 represent a slight decrease from 2.5 million in 2019, but the WHO considers the incidence high.
The organization’s updated statistics indicate that about 254 million people had hepatitis B in 2022, while 50 million had type C.
“Besides the deaths, the number of new cases every year is also striking. These are diseases that continue to spread. In the case of hepatitis C, the spread results from lack of access to disposable or properly sterilized sharp materials,” said Thor Dantas, MD, PhD, a physician and director of the Brazilian Society of Hepatology’s Viral Hepatitis Committee.
The situation of hepatitis B is particularly problematic, given that there is a safe and effective vaccine against it, said Dantas. “It’s remarkable that we continue to have so many new cases worldwide. This shows that we are failing in access to preventive measures for control and spread.”
Half of chronic hepatitis B and C cases occur in people between ages 30 and 54 years, while 12% affect children. There are more infections among men, who represent 58% of all cases.
The WHO also drew attention to the difficulty of accessing diagnosis and treatment. Only 13% of people with chronic hepatitis B infection were diagnosed, while only 3% — equivalent to 7 million people — received antiviral therapy by the end of 2022. This result is well below the WHO’s global target, which aims to treat 80% of cases by 2030.
Brazil has a higher diagnostic rate than the global average but is still below the target. According to the report, in 2022, the country diagnosed 34.2% of all hepatitis B infections. However, treatment coverage remains low: 3.6% of the total.
For hepatitis C, the scenario is somewhat different. During the same period, Brazil diagnosed 36% of total cases, with a treatment rate of 24%.
In 2022, Brazil had 2578 deaths from hepatitis B and 2977 from hepatitis C.
Because hepatitis is a silent disease, diagnosis often comes late, when the disease is already quite advanced, said Dr. Dantas. “Viral hepatitis evolves over the years essentially asymptomatically. Malaria shows symptoms, and tuberculosis shows symptoms. Viral hepatitis does not. They are only discovered through active searching.”
The WHO report shows significant regional differences in infection rates. Almost two thirds of cases are concentrated in the following 10 countries: China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Russia.
In terms of hepatitis C incidence, Brazil ranks 15th globally, with 536,000 cases in 2022, representing 1.1% of the global total. The list is led by Pakistan, with 8.8 million cases, equivalent to 17.8% of the total. Next are India, with 5.5 million (11.2%), and China, with 4 million (8.1%).
In addition to regional differences, the report also reveals profound disparities in the prices paid for major treatments.
“Price disparities between, and even within, WHO regions persist, with many countries paying above global reference values, including for nonpatented medications,” according to the report.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167849</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FCC5.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FCC5</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T164356</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T164404</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T164404</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T164404</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Giuliana Miranda</byline> <bylineText>GIULIANA MIRANDA</bylineText> <bylineFull>GIULIANA MIRANDA</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The report reveals that despite advances in diagnostic tools and treatment options, global treatment rates and coverage for detection tests have stagnated.</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>WHO’s World Hepatitis Summit finds that diagnosis and treatments have improved, yet testing and utilized therapies have stalled.</teaser> <title>Hepatitis Kills 3500 People Each Day, Says WHO</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">20</term> <term>21</term> <term>15</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">314</term> <term>234</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Hepatitis Kills 3500 People Each Day, Says WHO</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><br/><br/>The number of deaths from <span class="Hyperlink">viral hepatitis</span> worldwide increased from 1.1 million in 2019 to 1.3 million in 2022. These figures equate to approximately 3500 deaths per day due to the disease, which is the second leading cause of mortality from infectious agents globally.<br/><br/>These data are part of the recently released <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672">Global Hepatitis Report 2024</a></span>, which was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) during the World Hepatitis Summit in Lisbon, Portugal.<br/><br/><span class="tag metaDescription">The report reveals that despite advances in diagnostic tools and treatment options, global treatment rates and coverage for detection tests have stagnated.</span><br/><br/>“This report paints a concerning picture: Despite global progress in preventing hepatitis infections, deaths are increasing because very few people with hepatitis are being diagnosed and treated,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.<br/><br/><span class="Hyperlink">Hepatitis B</span> significantly is associated with the highest mortality rate. It accounted for 83% of deaths from the disease in 2022. Meanwhile, <span class="Hyperlink">hepatitis C</span> was responsible for 17% of deaths. The mortality of other, less common types of hepatitis was not considered in the ranking.<br/><br/>The report also indicates that more than 6000 people worldwide are infected with viral hepatitis every day. The 2.2 million new cases in 2022 represent a slight decrease from 2.5 million in 2019, but the WHO considers the incidence high.<br/><br/>The organization’s updated statistics indicate that about 254 million people had hepatitis B in 2022, while 50 million had type C.<br/><br/>“Besides the deaths, the number of new cases every year is also striking. These are diseases that continue to spread. In the case of hepatitis C, the spread results from lack of access to disposable or properly sterilized sharp materials,” said Thor Dantas, MD, PhD, a physician and director of the Brazilian Society of Hepatology’s Viral Hepatitis Committee.<br/><br/>The situation of hepatitis B is particularly problematic, given that there is a safe and effective vaccine against it, said Dantas. “It’s remarkable that we continue to have so many new cases worldwide. This shows that we are failing in access to preventive measures for control and spread.”<br/><br/>Half of chronic hepatitis B and C cases occur in people between ages 30 and 54 years, while 12% affect children. There are more infections among men, who represent 58% of all cases.<br/><br/>The WHO also drew attention to the difficulty of accessing diagnosis and treatment. Only 13% of people with chronic hepatitis B infection were diagnosed, while only 3% — equivalent to 7 million people — received antiviral therapy by the end of 2022. This result is well below the WHO’s global target, which aims to treat 80% of cases by 2030.<br/><br/>Brazil has a higher diagnostic rate than the global average but is still below the target. According to the report, in 2022, the country diagnosed 34.2% of all hepatitis B infections. However, treatment coverage remains low: 3.6% of the total.<br/><br/>For hepatitis C, the scenario is somewhat different. During the same period, Brazil diagnosed 36% of total cases, with a treatment rate of 24%.<br/><br/>In 2022, Brazil had 2578 deaths from hepatitis B and 2977 from hepatitis C.<br/><br/>Because hepatitis is a silent disease, diagnosis often comes late, when the disease is already quite advanced, said Dr. Dantas. “Viral hepatitis evolves over the years essentially asymptomatically. <span class="Hyperlink">Malaria</span> shows symptoms, and <span class="Hyperlink">tuberculosis</span> shows symptoms. Viral hepatitis does not. They are only discovered through active searching.”<br/><br/>The WHO report shows significant regional differences in infection rates. Almost two thirds of cases are concentrated in the following 10 countries: China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Russia.<br/><br/>In terms of hepatitis C incidence, Brazil ranks 15th globally, with 536,000 cases in 2022, representing 1.1% of the global total. The list is led by Pakistan, with 8.8 million cases, equivalent to 17.8% of the total. Next are India, with 5.5 million (11.2%), and China, with 4 million (8.1%).<br/><br/>In addition to regional differences, the report also reveals profound disparities in the prices paid for major treatments.<br/><br/>“Price disparities between, and even within, WHO regions persist, with many countries paying above global reference values, including for nonpatented medications,” according to the report.<br/><br/></p> <p> <em>This story was translated from the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://portugues.medscape.com/verartigo/6510952">Medscape Portuguese</a></span> edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/hepatitis-kills-3-5-million-people-each-day-says-who-2024a10007xi?src=">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167845</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FCA7.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FCA7</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T155925</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T155933</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T155933</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T155933</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Nicole Pajer</byline> <bylineText>NICOLE PAJER</bylineText> <bylineFull>NICOLE PAJER</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>We asked five veteran doctors who have supervised scores of young medical professionals over the years to tell us about that one person who impressed the hell o</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>Young doctors who got noticed shared their goals, followed through on their career passions, and made patients feel heard.</teaser> <title>How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>6</term> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>20</term> <term>15</term> <term>31</term> <term>25</term> <term>23</term> <term>52226</term> <term>18</term> <term>13</term> <term>34</term> <term>5</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?</p> <p><span class="tag metaDescription">We asked five veteran doctors who have supervised scores of young medical professionals over the years to tell us about that one person who impressed the hell out of them — what they did, why it made them game changers, and what every doctor can learn from them.</span> Here’s what they said ...<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask</h2> <p><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.tuftsmedicine.org/doctor/brien-barnewolt">Brien Barnewolt, MD</a></span>, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.<br/><br/>“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”<br/><br/>Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.<br/><br/>As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.<br/><br/>The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://physiciandirectory.brighamandwomens.org/details/12465/scott-weiner-emergency_medicine-boston">Dr. Weiner is currently</a></span> McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)<br/><br/>Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.<br/><br/>“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’</h2> <p><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medicine.duke.edu/profile/vance-garrison-fowler">Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS</a></span>, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant <em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.<br/><br/>So when <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medschool.duke.edu/stories/fighting-chance-against-infection">Tori Kinamon</a></span> asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral <span class="Hyperlink">osteomyelitis</span>, a bone infection that can coincide with <em>S aureus</em>. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.<br/><br/>“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.<br/><br/>She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.<br/><br/>Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”<br/><br/>If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something</h2> <p>As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.feinberg.northwestern.edu/faculty-profiles/az/profile.html?xid=10309">Scott Budinger, MD,</a></span> often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it. <br/><br/><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.nm.org/doctors/1760821474/justin-anthony-fiala-md">Justin Fiala, MD</a></span>, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.<br/><br/>Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.<br/><br/>“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.<br/><br/>Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.<br/><br/>“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”<br/><br/>The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.<br/><br/>“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person</h2> <p>When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.<br/><br/>“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.<br/><br/>Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.<br/><br/>“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”<br/><br/>Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient</h2> <p>Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.<br/><br/>“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medicine.yale.edu/profile/elizabeth-prsic/">Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD</a></span>, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.<br/><br/>Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.<br/><br/>This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.<br/><br/>“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”<br/><br/>Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”<br/><br/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/how-these-young-mds-impressed-hell-out-their-bosses-2024a10007wr">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Syphilis Treatment Falls Short for Pregnant Patients
Approximately one third of pregnant individuals with syphilis were inadequately treated or not treated for syphilis despite receiving timely prenatal care, based on data from nearly 1500 patients.
Although congenital syphilis is preventable with treatment before or early in pregnancy, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show a doubling of syphilis rates in the United States between 2018 and 2021 wrote Ayzsa Tannis, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
To better understand factors contributing to inadequate syphilis treatment during pregnancy, the researchers examined data from 1476 individuals with syphilis during pregnancy. The study population came from six jurisdictions that participated in the Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Pregnant People and Infants Network, and sources included case investigations, medical records, and links between laboratory data and vital records.
The researchers characterized the status of syphilis during pregnancy as adequate, inadequate, or not treated based on the CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Prenatal care was defined as timely (at least 30 days prior to pregnancy outcome), nontimely (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome), and no prenatal care. The findings were published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Of the 1476 individuals studied, 855 (57.9%) were adequately treated for syphilis and 621 (42.1%) were inadequately or not treated.
Overall, 82% of the study population received timely prenatal care. However, 32.1% of those who received timely prenatal care were inadequately treated, including 14.8% who received no syphilis treatment. Individuals with nontimely or no prenatal care were significantly more likely to receive inadequate or no treatment for syphilis than those who received timely care (risk ratio, 2.50 and 2.73, respectively).
The findings were consistent with previous studies of missed opportunities for prevention and treatment, the researchers noted. Factors behind nontimely treatment (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome) may include intermittent shortages of benzathine penicillin G, the standard treatment for syphilis, as well as the lack of time and administrative support for clinicians to communicate with patients and health departments, and to expedite treatment, the researchers wrote.
The results were limited by several factors including the use of data from six US jurisdictions that may not generalize to other areas, the variations in reporting years for the different jurisdictions, and variation in mandates for syphilis screening during pregnancy, the researchers noted.
More research is needed to improve syphilis testing itself, and to develop more treatment options, the researchers concluded. Partnerships among public health, patient advocacy groups, prenatal care clinicians, and other clinicians outside the prenatal care setting also are needed for effective intervention in pregnant individuals with syphilis, they said.
The study was carried out as part of the regular work of the CDC, supported by the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement and through contractual mechanisms including the Local Health Department Initiative to Chickasaw Health Consulting. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Approximately one third of pregnant individuals with syphilis were inadequately treated or not treated for syphilis despite receiving timely prenatal care, based on data from nearly 1500 patients.
Although congenital syphilis is preventable with treatment before or early in pregnancy, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show a doubling of syphilis rates in the United States between 2018 and 2021 wrote Ayzsa Tannis, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
To better understand factors contributing to inadequate syphilis treatment during pregnancy, the researchers examined data from 1476 individuals with syphilis during pregnancy. The study population came from six jurisdictions that participated in the Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Pregnant People and Infants Network, and sources included case investigations, medical records, and links between laboratory data and vital records.
The researchers characterized the status of syphilis during pregnancy as adequate, inadequate, or not treated based on the CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Prenatal care was defined as timely (at least 30 days prior to pregnancy outcome), nontimely (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome), and no prenatal care. The findings were published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Of the 1476 individuals studied, 855 (57.9%) were adequately treated for syphilis and 621 (42.1%) were inadequately or not treated.
Overall, 82% of the study population received timely prenatal care. However, 32.1% of those who received timely prenatal care were inadequately treated, including 14.8% who received no syphilis treatment. Individuals with nontimely or no prenatal care were significantly more likely to receive inadequate or no treatment for syphilis than those who received timely care (risk ratio, 2.50 and 2.73, respectively).
The findings were consistent with previous studies of missed opportunities for prevention and treatment, the researchers noted. Factors behind nontimely treatment (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome) may include intermittent shortages of benzathine penicillin G, the standard treatment for syphilis, as well as the lack of time and administrative support for clinicians to communicate with patients and health departments, and to expedite treatment, the researchers wrote.
The results were limited by several factors including the use of data from six US jurisdictions that may not generalize to other areas, the variations in reporting years for the different jurisdictions, and variation in mandates for syphilis screening during pregnancy, the researchers noted.
More research is needed to improve syphilis testing itself, and to develop more treatment options, the researchers concluded. Partnerships among public health, patient advocacy groups, prenatal care clinicians, and other clinicians outside the prenatal care setting also are needed for effective intervention in pregnant individuals with syphilis, they said.
The study was carried out as part of the regular work of the CDC, supported by the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement and through contractual mechanisms including the Local Health Department Initiative to Chickasaw Health Consulting. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Approximately one third of pregnant individuals with syphilis were inadequately treated or not treated for syphilis despite receiving timely prenatal care, based on data from nearly 1500 patients.
Although congenital syphilis is preventable with treatment before or early in pregnancy, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show a doubling of syphilis rates in the United States between 2018 and 2021 wrote Ayzsa Tannis, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
To better understand factors contributing to inadequate syphilis treatment during pregnancy, the researchers examined data from 1476 individuals with syphilis during pregnancy. The study population came from six jurisdictions that participated in the Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Pregnant People and Infants Network, and sources included case investigations, medical records, and links between laboratory data and vital records.
The researchers characterized the status of syphilis during pregnancy as adequate, inadequate, or not treated based on the CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Prenatal care was defined as timely (at least 30 days prior to pregnancy outcome), nontimely (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome), and no prenatal care. The findings were published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Of the 1476 individuals studied, 855 (57.9%) were adequately treated for syphilis and 621 (42.1%) were inadequately or not treated.
Overall, 82% of the study population received timely prenatal care. However, 32.1% of those who received timely prenatal care were inadequately treated, including 14.8% who received no syphilis treatment. Individuals with nontimely or no prenatal care were significantly more likely to receive inadequate or no treatment for syphilis than those who received timely care (risk ratio, 2.50 and 2.73, respectively).
The findings were consistent with previous studies of missed opportunities for prevention and treatment, the researchers noted. Factors behind nontimely treatment (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome) may include intermittent shortages of benzathine penicillin G, the standard treatment for syphilis, as well as the lack of time and administrative support for clinicians to communicate with patients and health departments, and to expedite treatment, the researchers wrote.
The results were limited by several factors including the use of data from six US jurisdictions that may not generalize to other areas, the variations in reporting years for the different jurisdictions, and variation in mandates for syphilis screening during pregnancy, the researchers noted.
More research is needed to improve syphilis testing itself, and to develop more treatment options, the researchers concluded. Partnerships among public health, patient advocacy groups, prenatal care clinicians, and other clinicians outside the prenatal care setting also are needed for effective intervention in pregnant individuals with syphilis, they said.
The study was carried out as part of the regular work of the CDC, supported by the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement and through contractual mechanisms including the Local Health Department Initiative to Chickasaw Health Consulting. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167766</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FABE.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FABE</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname>syphilis4.17.24</storyname> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T121054</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T123826</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T123826</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T123826</CMSDate> <articleSource>FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY</articleSource> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Heidi Splete</byline> <bylineText>HEIDI SPLETE</bylineText> <bylineFull>HEIDI SPLETE</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText>MDedge News</bylineTitleText> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType/> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>Approximately one third of pregnant individuals with syphilis were inadequately treated or not treated for syphilis despite receiving timely prenatal care, base</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>Potential challenges to effective treatment of syphilis in pregnancy include drug shortages and time constraints.</teaser> <title>Syphilis Treatment Falls Short for Pregnant Patients</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>15</term> <term canonical="true">20</term> <term>23</term> </publications> <sections> <term>27970</term> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term>234</term> <term>322</term> <term>280</term> <term>271</term> <term canonical="true">50729</term> <term>294</term> <term>71135</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Syphilis Treatment Falls Short for Pregnant Patients</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Approximately one third of pregnant individuals with syphilis were inadequately treated or not treated for syphilis despite receiving timely prenatal care, based on data from nearly 1500 patients.</p> <p>Although congenital syphilis is preventable with treatment before or early in pregnancy, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show a doubling of syphilis rates in the United States between 2018 and 2021 wrote Ayzsa Tannis, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.<br/><br/>To better understand factors contributing to inadequate syphilis treatment during pregnancy, the researchers examined data from 1476 individuals with syphilis during pregnancy. The study population came from six jurisdictions that participated in the Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Pregnant People and Infants Network, and sources included case investigations, medical records, and links between laboratory data and vital records.<br/><br/>The researchers characterized the status of syphilis during pregnancy as adequate, inadequate, or not treated based on the CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021. Prenatal care was defined as timely (at least 30 days prior to pregnancy outcome), nontimely (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome), and no prenatal care. The <span class="Hyperlink">findings</span> <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://journals.lww.com/greenjournal/abstract/9900/syphilis_treatment_among_people_who_are_pregnant.1059.aspx">were published</a></span> in <em>Obstetrics & Gynecology</em>. <br/><br/>Of the 1476 individuals studied, 855 (57.9%) were adequately treated for syphilis and 621 (42.1%) were inadequately or not treated.<br/><br/>Overall, 82% of the study population received timely prenatal care. However, 32.1% of those who received timely prenatal care were inadequately treated, including 14.8% who received no syphilis treatment. Individuals with nontimely or no prenatal care were significantly more likely to receive inadequate or no treatment for syphilis than those who received timely care (risk ratio, 2.50 and 2.73, respectively).<br/><br/>The findings were consistent with previous studies of missed opportunities for prevention and treatment, the researchers noted. Factors behind nontimely treatment (less than 30 days before pregnancy outcome) may include intermittent shortages of benzathine penicillin G, the standard treatment for syphilis, as well as the lack of time and administrative support for clinicians to communicate with patients and health departments, and to expedite treatment, the researchers wrote.<br/><br/>The results were limited by several factors including the use of data from six US jurisdictions that may not generalize to other areas, the variations in reporting years for the different jurisdictions, and variation in mandates for syphilis screening during pregnancy, the researchers noted.<br/><br/>More research is needed to improve syphilis testing itself, and to develop more treatment options, the researchers concluded. Partnerships among public health, patient advocacy groups, prenatal care clinicians, and other clinicians outside the prenatal care setting also are needed for effective intervention in pregnant individuals with syphilis, they said.<br/><br/>The study was carried out as part of the regular work of the CDC, supported by the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement and through contractual mechanisms including the Local Health Department Initiative to Chickasaw Health Consulting. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.<span class="end"/></p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167842</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FC9A.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FC9A</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T122750</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T122826</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T122826</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T122826</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Steph Weber</byline> <bylineText>STEPH WEBER</bylineText> <bylineFull>STEPH WEBER</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>Feature</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) voted Tuesday to ban noncompete agreements, possibly making it easier for doctors to switch employers without having to leave</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>But dissenting commissioners dispute the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.</teaser> <title>Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>icymicov</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdid</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>GIHOLD</publicationCode> <pubIssueName>January 2014</pubIssueName> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>5</term> <term>34</term> <term>6</term> <term>9</term> <term>13</term> <term canonical="true">15</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>21</term> <term>26</term> <term>31</term> <term>23</term> <term>25</term> <term>22</term> <term>52226</term> <term>69586</term> <term>58877</term> <term>51892</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">27980</term> <term>39313</term> <term>26933</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> <term>50194</term> <term>63993</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><span class="tag metaDescription">The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) voted Tuesday to ban noncompete agreements, possibly making it easier for doctors to switch employers without having to leave their communities and patients behind.</span> But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.</p> <p>The <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2024/04/ftc-announces-rule-banning-noncompetes">proposed final rule</a></span> passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.<br/><br/>Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/07/09/executive-order-on-promoting-competition-in-the-american-economy/">executive order</a></span> supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/986904">proposed ending the restrictive covenants</a></span>.<br/><br/>While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.<br/><br/>US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.uschamber.com/finance/antitrust/u-s-chamber-to-sue-ftc-over-unlawful-power-grab-on-noncompete-agreements-ban">statement</a></span> that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.<br/><br/>The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.<br/><br/>Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/urologist-sues-health-system-over-noncompete-clause-2024a1000389">risk expensive litigation</a></span> for wanting to pursue job opportunities.<br/><br/>For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/hospital-mergers-2024-five-things-know-2024a100047m">hospital systems merging</a></span>, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/some-mds-long-covid-burnout-new-reality-2024a10006hq">significant burnout</a></span> that can shorten their [career] longevity.”<br/><br/>Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/989694">lives upended</a></span> by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.<br/><br/>It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.<br/><br/>“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/senate-bill/483">Workforce Mobility Act of 2021</a></span> and the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/senate-bill/379">Freedom to Compete Act of 2023</a></span>.<br/><br/>The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.<br/><br/></p> <h2>States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes</h2> <p>Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the <em>Journal of the American College of Cardiology</em>, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100547">12 states</a></span> prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.<br/><br/>The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.oregon.gov/boli/employers/pages/noncompetition-agreements.aspx">Oregon</a></span>, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://oag.dc.gov/blog/worker-alert-noncompete-provisions-are-now-illegal">2-year noncompetes</a></span> for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.<br/><br/>Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://iga.in.gov/legislative/2023/bills/senate/7/details">primary care providers</a></span>. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/994478">terminates the contract for cause</a></span> or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.<br/><br/>Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.<br/><br/>Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.<br/><br/>Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ama-assn.org/medical-residents/transition-resident-attending/ama-backs-effort-ban-many-physician-noncompete">adopted policies</a></span> last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Challenges Await</h2> <p>The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.aha.org/press-releases/2024-04-23-aha-statement-final-ftc-noncompete-regulation">statement</a></span>.<br/><br/>To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ftc.gov/legal-library/browse/rules/noncompete-rule">model language</a></span> for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.<br/><br/>Dr. Marcus hopes the ban <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/are-you-ready-ai-be-better-doctor-than-you-2024a100070q">improves doctors’ lives</a></span>. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/federal-trade-commission-bans-noncompete-agreements-urges-2024a10007y0">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.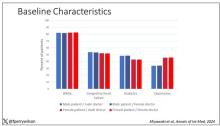
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 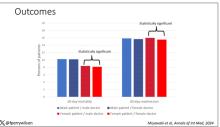
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167829</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FC71.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FC71</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T111623</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T113542</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T113542</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T113541</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>F. Perry Wilson, MD</byline> <bylineText>F. PERRY WILSON, MD, MSCE</bylineText> <bylineFull>F. PERRY WILSON, MD, MSCE</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>Female patients had a significantly lower 30-day mortality rate than male patients, but they fared even better when cared for by female doctors compared with ma</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage>301165</teaserImage> <teaser>Study finds female hospitalists provided better care, defined as lower 30-day mortality, than male hospitalists.</teaser> <title>Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>15</term> <term>5</term> <term>6</term> <term>34</term> <term>9</term> <term>13</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>52226</term> <term>31</term> <term>22</term> <term>25</term> <term>23</term> <term>58877</term> <term>26</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links> <link> <itemClass qcode="ninat:picture"/> <altRep contenttype="image/jpeg">images/24012878.jpg</altRep> <description role="drol:caption"/> <description role="drol:credit">Dr. Wilson</description> </link> <link> <itemClass qcode="ninat:picture"/> <altRep contenttype="image/jpeg">images/24012879.jpg</altRep> <description role="drol:caption"/> <description role="drol:credit">Dr. Wilson</description> </link> </links> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><br/><br/><em>This transcript has been edited for clarity</em>.</p> <p>It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?</p> <p>On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.<br/><br/>But this <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-3163">study</a></span>, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in <em>Annals of Internal Medicine</em>, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.<br/><br/>In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.<br/><br/>Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.<br/><br/>The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:</p> <ul class="body"> <li>Male patient – male doctor</li> <li>Male patient – female doctor</li> <li>Female patient – male doctor</li> <li>Female patient – female doctor</li> </ul> <p>The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.<br/><br/>I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.<br/><br/>[[{"fid":"301165","view_mode":"medstat_image_full_text","fields":{"format":"medstat_image_full_text","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":"Baseline characteristics","field_file_image_credit[und][0][value]":"Dr. Wilson","field_file_image_caption[und][0][value]":""},"type":"media","attributes":{"class":"media-element file-medstat_image_full_text"}}]]<br/><br/>Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.<br/><br/>So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.<br/><br/>I’ve graphed the results here. <span class="tag metaDescription">Female patients had a significantly lower 30-day mortality rate than male patients, but they fared even better when cared for by female doctors compared with male doctors. There wasn’t a particularly strong influence of physician sex on outcomes for male patients. The secondary outcome, 30-day hospital readmission, showed a similar trend.</span><br/><br/>[[{"fid":"301166","view_mode":"medstat_image_full_text","fields":{"format":"medstat_image_full_text","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":"Outcomes","field_file_image_credit[und][0][value]":"Dr. Wilson","field_file_image_caption[und][0][value]":""},"type":"media","attributes":{"class":"media-element file-medstat_image_full_text"}}]]<br/><br/>This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.<br/><br/>So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.<br/><br/>Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?<br/><br/>The authors cite <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3690315/">data that suggest</a></span> that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?<br/><br/>The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.<br/><br/>The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/647734">some prior studies have shown</a></span>. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.<br/><br/>Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?<br/><br/>And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.<br/><br/>Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.</em> </p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/1000715">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Menopause, RSV, and More: 4 New Meds to Know
BOSTON — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 55 new medications in 2023 and 11 more in 2024 to date.
A New First-Line for GERD?
Vonoprazan, an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker — which received FDA approval in November 2023 — may be a good alternative for patients whose symptoms continue to linger despite taking medications designated to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
GERD is the most common gastrointestinal symptom encountered by primary care physicians. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the first-line treatment for the condition but can have long-term side effects such as Clostridioides difficile infection and kidney lesions.
“We know that not all patients are going to have symptom relief with H2 blockers and PPIs, so there’s an opportunity for patients who don’t get full symptom relief,” Dr. Smetana told attendees.
Vonoprazan blocks potassium binding to ATPase proton pumps and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid.
The approval of vonoprazan for erosive GERD was based on results from the phase 3 PHALCON-EE study, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study that found the drug to be more effective than lansoprazole in treating erosive esophagitis.
Vonoprazan “has more rapid absorption than PPIs [and a] longer half-life and is more potent than PPIs, so theoretically it could be more effective in certain settings,” Dr. Smetana said.
Vonoprazan is FDA approved for only 6 months of use. Despite its efficacy, cost may be a barrier to many patients. H2 blockers generally cost patients less than $10 for 1 month’s supply, whereas vonoprazan can cost up to $650.
Nonhormonal Drug for Menopause
Fezolinetant, the first neurokinin receptor antagonist to receive approval from the FDA to treat vasomotor symptoms, may be an option for women concerned about hormone-based therapy for menopausal hot flashes.
“[Fezolinetant] specifically works in the area of the brain that’s involved in body temperature regulation and sweating,” Dr. Smetana said.
Results from the SKYLIGHT 1 randomized controlled trial of fezolinetant found the medication reduced the frequency and severity of hot flashes. Some of the side effects include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and insomnia.
Other nonestrogen treatments, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), gabapentin, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and hypnosis, are modestly effective, according to the North American Menopause Society.
“[Fezolinetant] offers a different option that physicians may be more comfortable prescribing,” Dr. Smetana said. “And I think this will be an important addition to nonhormonal therapy.”
RSV Vaccine for Everyone
Once considered an illness that is more prevalent in young children, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has become more prevalent and severe among older adults. Between 60,000 and 120,000 older adults are hospitalized and 6000-10,000 die of RSV infection each year, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The FDA has approved two RSV vaccines approved for older adults, but clinicians may find it challenging to get older patients vaccinated for this and other preventable illnesses.
Patients who received the RSV vaccine had an 83% relative risk reduction for the illness, according to a recent study, and an overall lower risk for hospitalization.
Moderna is developing an mRNA vaccine for RSV that is similar to many COVID-19 vaccines. A study published in 2023 in The New England Journal of Medicine found no cases of neuroinflammatory disorders among patients who received the mRNA RSV vaccine, with a median follow-up of 112 days.
“This is important given ongoing concerns of neurological safety,” among older adults who receive the RSV vaccine, Dr. Smetana said.
As of March 2024, the CDC recommends shared decision-making for adults older than 60 years and for healthcare providers to “consider” rather than “recommend” the vaccine for their patients. The agency’s Adult RSV Work Group plans to meet at June 2024 to reconsider whether shared clinical decision-making remains the preferred policy option.
New Antidepressants
A medication thrice rejected by the FDA is now heading a new class of drugs to treat major depressive disorder.
Gepirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, has a different mechanism of action from that of SSRIs, which are currently considered the first-line treatment for depression.
Gepirone was rejected by the FDA in 2002, 2004, and 2007, with concerns that the efficacy studies were too small. In 2015, an FDA advisory committee agreed that the evidence to date did not support approval of an extended-release form of the drug. But the agency decided to approve the medication in September 2023.
“So why is this medication worth discussing now?” Dr. Smetana said. “It’s because the side effect profile is different from existing antidepressants.”
Many patients may stop using SSRIs because of side effects such as insomnia and loss of libido, Dr. Smetana said. Gepirone has the potential to avoid activation of other 5-HT receptors that mediate side effects, he said.
Studies suggest that gepirone reduces both anxiety and depression scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in patients who have both conditions and decreases rates of depression relapse compared with placebo through at least 48 weeks. The drug also may be less likely than SSRIs to cause sexual dysfunction in men, Dr. Smetana said.
Gepirone will be available to prescribe to patients in fall 2024.
Dr. Smetana reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 55 new medications in 2023 and 11 more in 2024 to date.
A New First-Line for GERD?
Vonoprazan, an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker — which received FDA approval in November 2023 — may be a good alternative for patients whose symptoms continue to linger despite taking medications designated to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
GERD is the most common gastrointestinal symptom encountered by primary care physicians. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the first-line treatment for the condition but can have long-term side effects such as Clostridioides difficile infection and kidney lesions.
“We know that not all patients are going to have symptom relief with H2 blockers and PPIs, so there’s an opportunity for patients who don’t get full symptom relief,” Dr. Smetana told attendees.
Vonoprazan blocks potassium binding to ATPase proton pumps and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid.
The approval of vonoprazan for erosive GERD was based on results from the phase 3 PHALCON-EE study, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study that found the drug to be more effective than lansoprazole in treating erosive esophagitis.
Vonoprazan “has more rapid absorption than PPIs [and a] longer half-life and is more potent than PPIs, so theoretically it could be more effective in certain settings,” Dr. Smetana said.
Vonoprazan is FDA approved for only 6 months of use. Despite its efficacy, cost may be a barrier to many patients. H2 blockers generally cost patients less than $10 for 1 month’s supply, whereas vonoprazan can cost up to $650.
Nonhormonal Drug for Menopause
Fezolinetant, the first neurokinin receptor antagonist to receive approval from the FDA to treat vasomotor symptoms, may be an option for women concerned about hormone-based therapy for menopausal hot flashes.
“[Fezolinetant] specifically works in the area of the brain that’s involved in body temperature regulation and sweating,” Dr. Smetana said.
Results from the SKYLIGHT 1 randomized controlled trial of fezolinetant found the medication reduced the frequency and severity of hot flashes. Some of the side effects include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and insomnia.
Other nonestrogen treatments, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), gabapentin, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and hypnosis, are modestly effective, according to the North American Menopause Society.
“[Fezolinetant] offers a different option that physicians may be more comfortable prescribing,” Dr. Smetana said. “And I think this will be an important addition to nonhormonal therapy.”
RSV Vaccine for Everyone
Once considered an illness that is more prevalent in young children, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has become more prevalent and severe among older adults. Between 60,000 and 120,000 older adults are hospitalized and 6000-10,000 die of RSV infection each year, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The FDA has approved two RSV vaccines approved for older adults, but clinicians may find it challenging to get older patients vaccinated for this and other preventable illnesses.
Patients who received the RSV vaccine had an 83% relative risk reduction for the illness, according to a recent study, and an overall lower risk for hospitalization.
Moderna is developing an mRNA vaccine for RSV that is similar to many COVID-19 vaccines. A study published in 2023 in The New England Journal of Medicine found no cases of neuroinflammatory disorders among patients who received the mRNA RSV vaccine, with a median follow-up of 112 days.
“This is important given ongoing concerns of neurological safety,” among older adults who receive the RSV vaccine, Dr. Smetana said.
As of March 2024, the CDC recommends shared decision-making for adults older than 60 years and for healthcare providers to “consider” rather than “recommend” the vaccine for their patients. The agency’s Adult RSV Work Group plans to meet at June 2024 to reconsider whether shared clinical decision-making remains the preferred policy option.
New Antidepressants
A medication thrice rejected by the FDA is now heading a new class of drugs to treat major depressive disorder.
Gepirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, has a different mechanism of action from that of SSRIs, which are currently considered the first-line treatment for depression.
Gepirone was rejected by the FDA in 2002, 2004, and 2007, with concerns that the efficacy studies were too small. In 2015, an FDA advisory committee agreed that the evidence to date did not support approval of an extended-release form of the drug. But the agency decided to approve the medication in September 2023.
“So why is this medication worth discussing now?” Dr. Smetana said. “It’s because the side effect profile is different from existing antidepressants.”
Many patients may stop using SSRIs because of side effects such as insomnia and loss of libido, Dr. Smetana said. Gepirone has the potential to avoid activation of other 5-HT receptors that mediate side effects, he said.
Studies suggest that gepirone reduces both anxiety and depression scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in patients who have both conditions and decreases rates of depression relapse compared with placebo through at least 48 weeks. The drug also may be less likely than SSRIs to cause sexual dysfunction in men, Dr. Smetana said.
Gepirone will be available to prescribe to patients in fall 2024.
Dr. Smetana reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 55 new medications in 2023 and 11 more in 2024 to date.
A New First-Line for GERD?
Vonoprazan, an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker — which received FDA approval in November 2023 — may be a good alternative for patients whose symptoms continue to linger despite taking medications designated to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
GERD is the most common gastrointestinal symptom encountered by primary care physicians. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the first-line treatment for the condition but can have long-term side effects such as Clostridioides difficile infection and kidney lesions.
“We know that not all patients are going to have symptom relief with H2 blockers and PPIs, so there’s an opportunity for patients who don’t get full symptom relief,” Dr. Smetana told attendees.
Vonoprazan blocks potassium binding to ATPase proton pumps and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid.
The approval of vonoprazan for erosive GERD was based on results from the phase 3 PHALCON-EE study, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study that found the drug to be more effective than lansoprazole in treating erosive esophagitis.
Vonoprazan “has more rapid absorption than PPIs [and a] longer half-life and is more potent than PPIs, so theoretically it could be more effective in certain settings,” Dr. Smetana said.
Vonoprazan is FDA approved for only 6 months of use. Despite its efficacy, cost may be a barrier to many patients. H2 blockers generally cost patients less than $10 for 1 month’s supply, whereas vonoprazan can cost up to $650.
Nonhormonal Drug for Menopause
Fezolinetant, the first neurokinin receptor antagonist to receive approval from the FDA to treat vasomotor symptoms, may be an option for women concerned about hormone-based therapy for menopausal hot flashes.
“[Fezolinetant] specifically works in the area of the brain that’s involved in body temperature regulation and sweating,” Dr. Smetana said.
Results from the SKYLIGHT 1 randomized controlled trial of fezolinetant found the medication reduced the frequency and severity of hot flashes. Some of the side effects include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and insomnia.
Other nonestrogen treatments, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), gabapentin, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and hypnosis, are modestly effective, according to the North American Menopause Society.
“[Fezolinetant] offers a different option that physicians may be more comfortable prescribing,” Dr. Smetana said. “And I think this will be an important addition to nonhormonal therapy.”
RSV Vaccine for Everyone
Once considered an illness that is more prevalent in young children, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has become more prevalent and severe among older adults. Between 60,000 and 120,000 older adults are hospitalized and 6000-10,000 die of RSV infection each year, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The FDA has approved two RSV vaccines approved for older adults, but clinicians may find it challenging to get older patients vaccinated for this and other preventable illnesses.
Patients who received the RSV vaccine had an 83% relative risk reduction for the illness, according to a recent study, and an overall lower risk for hospitalization.
Moderna is developing an mRNA vaccine for RSV that is similar to many COVID-19 vaccines. A study published in 2023 in The New England Journal of Medicine found no cases of neuroinflammatory disorders among patients who received the mRNA RSV vaccine, with a median follow-up of 112 days.
“This is important given ongoing concerns of neurological safety,” among older adults who receive the RSV vaccine, Dr. Smetana said.
As of March 2024, the CDC recommends shared decision-making for adults older than 60 years and for healthcare providers to “consider” rather than “recommend” the vaccine for their patients. The agency’s Adult RSV Work Group plans to meet at June 2024 to reconsider whether shared clinical decision-making remains the preferred policy option.
New Antidepressants
A medication thrice rejected by the FDA is now heading a new class of drugs to treat major depressive disorder.
Gepirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, has a different mechanism of action from that of SSRIs, which are currently considered the first-line treatment for depression.
Gepirone was rejected by the FDA in 2002, 2004, and 2007, with concerns that the efficacy studies were too small. In 2015, an FDA advisory committee agreed that the evidence to date did not support approval of an extended-release form of the drug. But the agency decided to approve the medication in September 2023.
“So why is this medication worth discussing now?” Dr. Smetana said. “It’s because the side effect profile is different from existing antidepressants.”
Many patients may stop using SSRIs because of side effects such as insomnia and loss of libido, Dr. Smetana said. Gepirone has the potential to avoid activation of other 5-HT receptors that mediate side effects, he said.
Studies suggest that gepirone reduces both anxiety and depression scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in patients who have both conditions and decreases rates of depression relapse compared with placebo through at least 48 weeks. The drug also may be less likely than SSRIs to cause sexual dysfunction in men, Dr. Smetana said.
Gepirone will be available to prescribe to patients in fall 2024.
Dr. Smetana reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167807</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FBBF.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FBBF</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240423T110410</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240423T114823</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240423T114823</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240423T114823</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Lara Salahi</byline> <bylineText>LARA SALAHI</bylineText> <bylineFull>LARA SALAHI</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>During a presentation on April 18 at the annual American College of Physicians Internal Medicine Meeting, Gerald Smetana, MD, professor of medicine in the Divis</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>New treatments have been approved to treat conditions including GERD, depression, RSV vaccines, and hot flashes with menopause.</teaser> <title>Menopause, RSV, and More: 4 New Meds to Know</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>23</term> <term>15</term> <term>20</term> <term>6</term> <term>9</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term>202</term> <term canonical="true">65668</term> <term>322</term> <term>247</term> <term>234</term> <term>248</term> <term>50347</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Menopause, RSV, and More: 4 New Meds to Know</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><span class="dateline">BOSTON</span> — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved <span class="Hyperlink">55 new medications</span> in 2023 and <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.fda.gov/drugs/novel-drug-approvals-fda/novel-drug-approvals-2024">11 more in 2024 to date</a></span>. <span class="tag metaDescription">During a presentation on April 18 at the annual American College of Physicians Internal Medicine Meeting, Gerald Smetana, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of General Medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, reviewed four of these new therapies that are likely to be particularly important for primary care clinicians. </span></p> <h2>A New First-Line for GERD?</h2> <p>Vonoprazan, an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker — which received<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/998031"> FDA approval in November 2023</a></span> — may be a good alternative for patients whose symptoms continue to linger despite taking medications designated to treat <span class="Hyperlink">gastroesophageal reflux disease</span> (GERD). <br/><br/>GERD is the<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30323268/"> most common</a></span> gastrointestinal symptom encountered by primary care physicians. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the first-line treatment for the condition but can have long-term side effects such as Clostridioides difficile infection and kidney lesions.<br/><br/>“We know that not all patients are going to have symptom relief with H2 blockers and PPIs, so there’s an opportunity for patients who don’t get full symptom relief,” Dr. Smetana told attendees. <br/><br/>Vonoprazan blocks potassium binding to ATPase proton pumps and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid.<br/><br/>The <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/998031">approval of vonoprazan</a></span> for erosive GERD was based on results from the phase 3 PHALCON-EE study, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study that found the drug to be more effective than <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://reference.medscape.com/drug/prevacid-solu-tab-lansoprazole-341991">lansoprazole</a></span> in treating erosive <span class="Hyperlink">esophagitis</span>.<br/><br/>Vonoprazan “has more rapid absorption than PPIs [and a] longer half-life and is more potent than PPIs, so theoretically it could be more effective in certain settings,” Dr. Smetana said.<br/><br/>Vonoprazan is FDA approved for only 6 months of use. Despite its efficacy, cost may be a barrier to many patients. H2 blockers generally cost patients less than $10 for 1 month’s supply, whereas vonoprazan can cost up to $650.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Nonhormonal Drug for Menopause</h2> <p><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/992670">Fezolinetant</a></span>, the first neurokinin receptor antagonist to receive <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-novel-drug-treat-moderate-severe-hot-flashes-caused-menopause">approval from the FDA</a></span> to treat vasomotor symptoms, may be an option for women concerned about hormone-based therapy for menopausal hot flashes.<br/><br/>“[Fezolinetant] specifically works in the area of the brain that’s involved in body temperature regulation and sweating,” Dr. Smetana said.<br/><br/>Results from the<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(23)00085-5/abstract"> SKYLIGHT 1</a></span> randomized controlled trial of fezolinetant found the medication reduced the frequency and severity of hot flashes. Some of the side effects include abdominal pain, <span class="Hyperlink">diarrhea</span>, and <span class="Hyperlink">insomnia</span>. <br/><br/>Other nonestrogen treatments, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), <span class="Hyperlink">gabapentin</span>, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and hypnosis, are modestly effective, according to the<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.menopause.org/for-women/menopause-faqs-hot-flashes"> North American Menopause Society</a></span>.<br/><br/>“[Fezolinetant] offers a different option that physicians may be more comfortable prescribing,” Dr. Smetana said. “And I think this will be an important addition to nonhormonal therapy.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>RSV Vaccine for Everyone </h2> <p>Once considered an illness that is more prevalent in young children, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has become more prevalent and severe among older adults. Between 60,000 and 120,000 older adults are hospitalized and 6000-10,000 die of RSV infection each year, according to the US<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/high-risk/older-adults.html"> Centers for Disease Control and Prevention</a></span>. <br/><br/>The FDA has approved<span class="Hyperlink"> two RSV vaccines</span> approved for older adults, but clinicians may find it challenging to get older patients vaccinated for this and other preventable illnesses.<br/><br/>Patients who received the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/994631">RSV vaccine</a></span> had an 83% relative risk reduction for the illness,<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36791160/"> according to a recent study</a></span>, and an overall lower risk for hospitalization.<br/><br/>Moderna is developing an mRNA vaccine for RSV that is similar to many COVID-19 vaccines.<span class="Hyperlink"> <a href="https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2307079">A study</a> published in 2023 in </span><em>The New England Journal of Medicine </em>found no cases of neuroinflammatory disorders among patients who received the mRNA RSV vaccine, with a median follow-up of 112 days.<br/><br/>“This is important given ongoing concerns of<span class="Hyperlink"> neurological safety</span>,” among older adults who receive the RSV vaccine, Dr. Smetana said.<br/><br/>As of March 2024, the CDC recommends shared decision-making for adults older than 60 years and for healthcare providers to “consider” rather than “recommend” the vaccine for their patients. The agency’s<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2024-02-28-29/08-RSV-Adults-Britton-508.pdf"> Adult RSV Work Group</a></span> plans to meet at June 2024 to reconsider whether shared clinical decision-making remains the preferred policy option.<br/><br/></p> <h2>New Antidepressants</h2> <p>A medication thrice rejected by the FDA is now heading a new class of drugs to treat major depressive disorder.<br/><br/><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://reference.medscape.com/drug/exxua-gepirone-1000091">Gepirone</a></span>, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, has a different mechanism of action from that of SSRIs, which are currently considered the first-line treatment for depression. <br/><br/>Gepirone was rejected by the FDA in 2002, 2004, and 2007, with concerns that the efficacy studies were too small. <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/855373">In 2015</a></span>, an FDA advisory committee agreed that the evidence to date did not support approval of an extended-release form of the drug. But the agency decided to approve the medication in September 2023.<br/><br/>“So why is this medication worth discussing now?” Dr. Smetana said. “It’s because the side effect profile is different from existing antidepressants.” <br/><br/>Many patients may stop using SSRIs because of side effects such as insomnia and loss of libido, Dr. Smetana said. Gepirone has the potential to avoid activation of other 5-HT receptors that mediate side effects, he said. <br/><br/>Studies suggest that gepirone <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11206598/">reduces both anxiety and depression scores</a></span> on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in patients who have both conditions and decreases rates of<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2943802/"> depression relapse</a></span> compared with placebo through at least 48 weeks. The drug also may be less likely than SSRIs to cause<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02624.x"> sexual dysfunction</a></span> in men, Dr. Smetana said. <br/><br/>Gepirone will be available to prescribe to patients in <span class="Hyperlink">fall 2024.<br/><br/></span>Dr. Smetana reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.<span class="end"/> <br/><br/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/menopause-rsv-and-more-4-new-meds-know-2024a10007m3">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
AI Surpasses Harvard Docs on Clinical Reasoning Test
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167792</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FB5E.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FB5E</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240422T151634</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240422T152509</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240422T152509</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240422T152509</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Edited by Jake Remaly</byline> <bylineText>EDITED JAKE REMALY</bylineText> <bylineFull>EDITED JAKE REMALY</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>A study comparing the clinical reasoning of an artificial intelligence (AI) model with that of physicians found the AI outperformed residents and attending phys</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>When compared to residents, AI more often used incorrect reasoning but overall scored higher in simulated cases, says a recent study.</teaser> <title>AI Surpasses Harvard Docs on Clinical Reasoning Test</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>5</term> <term>6</term> <term>34</term> <term>9</term> <term>13</term> <term>15</term> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>20</term> <term>52226</term> <term>22</term> <term>23</term> <term>31</term> <term>25</term> <term>26</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>AI Surpasses Harvard Docs on Clinical Reasoning Test</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <h2>TOPLINE: </h2> <p><span class="tag metaDescription">A study comparing the clinical reasoning of an artificial intelligence (AI) model with that of physicians found the AI outperformed residents and attending physicians in simulated cases.</span> The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.</p> <h2>METHODOLOGY:</h2> <ul class="body"> <li>The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.</li> <li>Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as <span class="Hyperlink">pharyngitis</span>, <span class="Hyperlink">headache</span>, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.</li> <li>The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.</li> </ul> <h2>TAKEAWAY: </h2> <ul class="body"> <li>AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).</li> <li>The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).</li> <li>AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.</li> </ul> <h2>IN PRACTICE:</h2> <p>“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote. </p> <h2>SOURCE:</h2> <p>Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2817046">was published online</a></span> in <em>JAMA Internal Medicine</em>. </p> <h2>LIMITATIONS: </h2> <p>Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted. </p> <h2>DISCLOSURES:</h2> <p>The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/ai-surpasses-harvard-docs-clinical-reasoning-test-2024a10007lf">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
