User login
Special Report II: Tackling Burnout
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
Ready for post-acute care?
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”
 122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
Hospitalists can fill a need
More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”
 122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
Hospitalists can fill a need
More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”
 122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
122259_Medicare_claims web.PNG
Hospitalists can fill a need
More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167861</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FD43.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FD43</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240426T111340</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240426T114737</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240426T114737</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240426T114737</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Jennifer Nelson</byline> <bylineText>JENNIFER NELSON</bylineText> <bylineFull>JENNIFER NELSON</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The switch is the first of its kind in the United States and comes on the heels of a decision from 2021 by the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA) t</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>In June, Oregon PAs will be referred to as Physician Associates, a title change from Physician Assistants being debated nationwide. </teaser> <title>Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>5</term> <term>6</term> <term>15</term> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>9</term> <term>34</term> <term>13</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>52226</term> <term>22</term> <term>23</term> <term>31</term> <term>25</term> <term>26</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.aapa.org/news-central/2024/04/oregon-governor-tina-kotek-signs-law-changing-pa-title/?utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=aapa_post&utm_campaign=news_central">bill</a></span> into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state. <span class="tag metaDescription">The switch is the first of its kind in the United States and comes on the heels of a decision from 2021 by the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA) to change the meaning of “PA” to “physician associate” from “physician assistant.”</span></p> <p>In the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/slideshow/2023-physician-assistant-satisfaction-6016503#2">Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023</a>, </span>a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.<br/><br/>According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/985263">working independently</a></span> with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.<br/><br/>Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.<br/><br/>Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.<br/><br/>Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.<br/><br/>The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/oregon-physician-assistants-get-name-change-2024a100084h">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167845</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FCA7.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FCA7</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T155925</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T155933</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T155933</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T155933</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Nicole Pajer</byline> <bylineText>NICOLE PAJER</bylineText> <bylineFull>NICOLE PAJER</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>We asked five veteran doctors who have supervised scores of young medical professionals over the years to tell us about that one person who impressed the hell o</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>Young doctors who got noticed shared their goals, followed through on their career passions, and made patients feel heard.</teaser> <title>How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>6</term> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>20</term> <term>15</term> <term>31</term> <term>25</term> <term>23</term> <term>52226</term> <term>18</term> <term>13</term> <term>34</term> <term>5</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?</p> <p><span class="tag metaDescription">We asked five veteran doctors who have supervised scores of young medical professionals over the years to tell us about that one person who impressed the hell out of them — what they did, why it made them game changers, and what every doctor can learn from them.</span> Here’s what they said ...<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask</h2> <p><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.tuftsmedicine.org/doctor/brien-barnewolt">Brien Barnewolt, MD</a></span>, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.<br/><br/>“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”<br/><br/>Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.<br/><br/>As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.<br/><br/>The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (<span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://physiciandirectory.brighamandwomens.org/details/12465/scott-weiner-emergency_medicine-boston">Dr. Weiner is currently</a></span> McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)<br/><br/>Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.<br/><br/>“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’</h2> <p><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medicine.duke.edu/profile/vance-garrison-fowler">Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS</a></span>, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant <em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.<br/><br/>So when <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medschool.duke.edu/stories/fighting-chance-against-infection">Tori Kinamon</a></span> asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral <span class="Hyperlink">osteomyelitis</span>, a bone infection that can coincide with <em>S aureus</em>. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.<br/><br/>“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.<br/><br/>She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.<br/><br/>Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”<br/><br/>If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something</h2> <p>As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.feinberg.northwestern.edu/faculty-profiles/az/profile.html?xid=10309">Scott Budinger, MD,</a></span> often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it. <br/><br/><span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.nm.org/doctors/1760821474/justin-anthony-fiala-md">Justin Fiala, MD</a></span>, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.<br/><br/>Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.<br/><br/>“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.<br/><br/>Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.<br/><br/>“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”<br/><br/>The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.<br/><br/>“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person</h2> <p>When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.<br/><br/>“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.<br/><br/>Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.<br/><br/>“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”<br/><br/>Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”<br/><br/></p> <h2>Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient</h2> <p>Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.<br/><br/>“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://medicine.yale.edu/profile/elizabeth-prsic/">Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD</a></span>, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.<br/><br/>Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.<br/><br/>This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.<br/><br/>“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”<br/><br/>Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”<br/><br/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/how-these-young-mds-impressed-hell-out-their-bosses-2024a10007wr">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167842</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FC9A.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FC9A</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T122750</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T122826</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T122826</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T122826</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Steph Weber</byline> <bylineText>STEPH WEBER</bylineText> <bylineFull>STEPH WEBER</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>Feature</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) voted Tuesday to ban noncompete agreements, possibly making it easier for doctors to switch employers without having to leave</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>But dissenting commissioners dispute the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.</teaser> <title>Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>icymicov</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdid</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>GIHOLD</publicationCode> <pubIssueName>January 2014</pubIssueName> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term>5</term> <term>34</term> <term>6</term> <term>9</term> <term>13</term> <term canonical="true">15</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>21</term> <term>26</term> <term>31</term> <term>23</term> <term>25</term> <term>22</term> <term>52226</term> <term>69586</term> <term>58877</term> <term>51892</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">27980</term> <term>39313</term> <term>26933</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> <term>50194</term> <term>63993</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><span class="tag metaDescription">The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) voted Tuesday to ban noncompete agreements, possibly making it easier for doctors to switch employers without having to leave their communities and patients behind.</span> But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.</p> <p>The <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2024/04/ftc-announces-rule-banning-noncompetes">proposed final rule</a></span> passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.<br/><br/>Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/07/09/executive-order-on-promoting-competition-in-the-american-economy/">executive order</a></span> supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/986904">proposed ending the restrictive covenants</a></span>.<br/><br/>While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.<br/><br/>US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.uschamber.com/finance/antitrust/u-s-chamber-to-sue-ftc-over-unlawful-power-grab-on-noncompete-agreements-ban">statement</a></span> that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.<br/><br/>The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.<br/><br/>Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/urologist-sues-health-system-over-noncompete-clause-2024a1000389">risk expensive litigation</a></span> for wanting to pursue job opportunities.<br/><br/>For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/hospital-mergers-2024-five-things-know-2024a100047m">hospital systems merging</a></span>, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/some-mds-long-covid-burnout-new-reality-2024a10006hq">significant burnout</a></span> that can shorten their [career] longevity.”<br/><br/>Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/989694">lives upended</a></span> by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.<br/><br/>It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.<br/><br/>“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/senate-bill/483">Workforce Mobility Act of 2021</a></span> and the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/senate-bill/379">Freedom to Compete Act of 2023</a></span>.<br/><br/>The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.<br/><br/></p> <h2>States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes</h2> <p>Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the <em>Journal of the American College of Cardiology</em>, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100547">12 states</a></span> prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.<br/><br/>The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.oregon.gov/boli/employers/pages/noncompetition-agreements.aspx">Oregon</a></span>, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://oag.dc.gov/blog/worker-alert-noncompete-provisions-are-now-illegal">2-year noncompetes</a></span> for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.<br/><br/>Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://iga.in.gov/legislative/2023/bills/senate/7/details">primary care providers</a></span>. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/994478">terminates the contract for cause</a></span> or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.<br/><br/>Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.<br/><br/>Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.<br/><br/>Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ama-assn.org/medical-residents/transition-resident-attending/ama-backs-effort-ban-many-physician-noncompete">adopted policies</a></span> last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Challenges Await</h2> <p>The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.aha.org/press-releases/2024-04-23-aha-statement-final-ftc-noncompete-regulation">statement</a></span>.<br/><br/>To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ftc.gov/legal-library/browse/rules/noncompete-rule">model language</a></span> for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.<br/><br/>Dr. Marcus hopes the ban <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/are-you-ready-ai-be-better-doctor-than-you-2024a100070q">improves doctors’ lives</a></span>. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/federal-trade-commission-bans-noncompete-agreements-urges-2024a10007y0">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.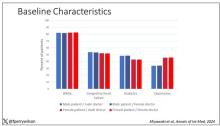
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 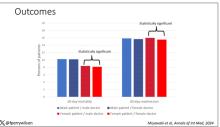
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167829</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FC71.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FC71</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T111623</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T113542</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T113542</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T113541</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>F. Perry Wilson, MD</byline> <bylineText>F. PERRY WILSON, MD, MSCE</bylineText> <bylineFull>F. PERRY WILSON, MD, MSCE</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>Female patients had a significantly lower 30-day mortality rate than male patients, but they fared even better when cared for by female doctors compared with ma</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage>301165</teaserImage> <teaser>Study finds female hospitalists provided better care, defined as lower 30-day mortality, than male hospitalists.</teaser> <title>Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>idprac</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>15</term> <term>5</term> <term>6</term> <term>34</term> <term>9</term> <term>13</term> <term>18</term> <term>20</term> <term>52226</term> <term>31</term> <term>22</term> <term>25</term> <term>23</term> <term>58877</term> <term>26</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links> <link> <itemClass qcode="ninat:picture"/> <altRep contenttype="image/jpeg">images/24012878.jpg</altRep> <description role="drol:caption"/> <description role="drol:credit">Dr. Wilson</description> </link> <link> <itemClass qcode="ninat:picture"/> <altRep contenttype="image/jpeg">images/24012879.jpg</altRep> <description role="drol:caption"/> <description role="drol:credit">Dr. Wilson</description> </link> </links> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p><br/><br/><em>This transcript has been edited for clarity</em>.</p> <p>It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?</p> <p>On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.<br/><br/>But this <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-3163">study</a></span>, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in <em>Annals of Internal Medicine</em>, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.<br/><br/>In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.<br/><br/>Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.<br/><br/>The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:</p> <ul class="body"> <li>Male patient – male doctor</li> <li>Male patient – female doctor</li> <li>Female patient – male doctor</li> <li>Female patient – female doctor</li> </ul> <p>The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.<br/><br/>I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.<br/><br/>[[{"fid":"301165","view_mode":"medstat_image_full_text","fields":{"format":"medstat_image_full_text","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":"Baseline characteristics","field_file_image_credit[und][0][value]":"Dr. Wilson","field_file_image_caption[und][0][value]":""},"type":"media","attributes":{"class":"media-element file-medstat_image_full_text"}}]]<br/><br/>Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.<br/><br/>So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.<br/><br/>I’ve graphed the results here. <span class="tag metaDescription">Female patients had a significantly lower 30-day mortality rate than male patients, but they fared even better when cared for by female doctors compared with male doctors. There wasn’t a particularly strong influence of physician sex on outcomes for male patients. The secondary outcome, 30-day hospital readmission, showed a similar trend.</span><br/><br/>[[{"fid":"301166","view_mode":"medstat_image_full_text","fields":{"format":"medstat_image_full_text","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":"Outcomes","field_file_image_credit[und][0][value]":"Dr. Wilson","field_file_image_caption[und][0][value]":""},"type":"media","attributes":{"class":"media-element file-medstat_image_full_text"}}]]<br/><br/>This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.<br/><br/>So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.<br/><br/>Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?<br/><br/>The authors cite <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3690315/">data that suggest</a></span> that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?<br/><br/>The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.<br/><br/>The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/647734">some prior studies have shown</a></span>. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.<br/><br/>Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?<br/><br/>And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.<br/><br/>Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.</em> </p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/1000715">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
FDA Approves New Bladder Cancer Drug
Specifically, the agent is approved to treat patients with BCG-unresponsive non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer carcinoma in situ with or without Ta or T1 papillary disease.
The FDA declined an initial approval for the combination in May 2023 because of deficiencies the agency observed during its prelicense inspection of third-party manufacturing organizations. In October 2023, ImmunityBio resubmitted the Biologics License Application, which was accepted.
The new therapy represents addresses “an unmet need” in this high-risk bladder cancer population, the company stated in a press release announcing the initial study findings. Typically, patients with intermediate or high-risk disease undergo bladder tumor resection followed by treatment with BCG, but the cancer recurs in up to 50% of patients, including those who experience a complete response, explained ImmunityBio, which acquired Altor BioScience.
Approval was based on findings from the single arm, phase 2/3 open-label QUILT-3.032 study, which included 77 patients with BCG-unresponsive, high-risk disease following transurethral resection. All had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2.
Patients received nogapendekin alfa inbakicept-pmln induction via intravesical instillation with BCG followed by maintenance therapy for up to 37 months.
According to the FDA’s press release, 62% of patients had a complete response, defined as a negative cystoscopy and urine cytology; 58% of those with a complete response had a duration of response lasting at least 12 months and 40% had a duration of response lasting 24 months or longer.
The safety of the combination was evaluated in a cohort of 88 patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included dysuria, pollakiuria, and hematuria, which are associated with intravesical BCG; 86% of these events were grade 1 or 2. Overall, 7% of patients discontinued the combination owing to adverse reactions.
The recommended dose is 400 mcg administered intravesically with BCG once a week for 6 weeks as induction therapy, with an option for a second induction course if patients don’t achieve a complete response at 3 months. The recommended maintenance therapy dose is 400 mcg with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 4, 7, 10, 13, and 19. Patients who achieve a complete response at 25 months and beyond may receive maintenance instillations with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 25, 31, and 37. The maximum treatment duration is 37 months.
The FDA recommends discontinuing treatment if disease persists after second induction or owing to disease recurrence, progression, or unacceptable toxicity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the agent is approved to treat patients with BCG-unresponsive non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer carcinoma in situ with or without Ta or T1 papillary disease.
The FDA declined an initial approval for the combination in May 2023 because of deficiencies the agency observed during its prelicense inspection of third-party manufacturing organizations. In October 2023, ImmunityBio resubmitted the Biologics License Application, which was accepted.
The new therapy represents addresses “an unmet need” in this high-risk bladder cancer population, the company stated in a press release announcing the initial study findings. Typically, patients with intermediate or high-risk disease undergo bladder tumor resection followed by treatment with BCG, but the cancer recurs in up to 50% of patients, including those who experience a complete response, explained ImmunityBio, which acquired Altor BioScience.
Approval was based on findings from the single arm, phase 2/3 open-label QUILT-3.032 study, which included 77 patients with BCG-unresponsive, high-risk disease following transurethral resection. All had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2.
Patients received nogapendekin alfa inbakicept-pmln induction via intravesical instillation with BCG followed by maintenance therapy for up to 37 months.
According to the FDA’s press release, 62% of patients had a complete response, defined as a negative cystoscopy and urine cytology; 58% of those with a complete response had a duration of response lasting at least 12 months and 40% had a duration of response lasting 24 months or longer.
The safety of the combination was evaluated in a cohort of 88 patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included dysuria, pollakiuria, and hematuria, which are associated with intravesical BCG; 86% of these events were grade 1 or 2. Overall, 7% of patients discontinued the combination owing to adverse reactions.
The recommended dose is 400 mcg administered intravesically with BCG once a week for 6 weeks as induction therapy, with an option for a second induction course if patients don’t achieve a complete response at 3 months. The recommended maintenance therapy dose is 400 mcg with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 4, 7, 10, 13, and 19. Patients who achieve a complete response at 25 months and beyond may receive maintenance instillations with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 25, 31, and 37. The maximum treatment duration is 37 months.
The FDA recommends discontinuing treatment if disease persists after second induction or owing to disease recurrence, progression, or unacceptable toxicity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the agent is approved to treat patients with BCG-unresponsive non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer carcinoma in situ with or without Ta or T1 papillary disease.
The FDA declined an initial approval for the combination in May 2023 because of deficiencies the agency observed during its prelicense inspection of third-party manufacturing organizations. In October 2023, ImmunityBio resubmitted the Biologics License Application, which was accepted.
The new therapy represents addresses “an unmet need” in this high-risk bladder cancer population, the company stated in a press release announcing the initial study findings. Typically, patients with intermediate or high-risk disease undergo bladder tumor resection followed by treatment with BCG, but the cancer recurs in up to 50% of patients, including those who experience a complete response, explained ImmunityBio, which acquired Altor BioScience.
Approval was based on findings from the single arm, phase 2/3 open-label QUILT-3.032 study, which included 77 patients with BCG-unresponsive, high-risk disease following transurethral resection. All had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2.
Patients received nogapendekin alfa inbakicept-pmln induction via intravesical instillation with BCG followed by maintenance therapy for up to 37 months.
According to the FDA’s press release, 62% of patients had a complete response, defined as a negative cystoscopy and urine cytology; 58% of those with a complete response had a duration of response lasting at least 12 months and 40% had a duration of response lasting 24 months or longer.
The safety of the combination was evaluated in a cohort of 88 patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included dysuria, pollakiuria, and hematuria, which are associated with intravesical BCG; 86% of these events were grade 1 or 2. Overall, 7% of patients discontinued the combination owing to adverse reactions.
The recommended dose is 400 mcg administered intravesically with BCG once a week for 6 weeks as induction therapy, with an option for a second induction course if patients don’t achieve a complete response at 3 months. The recommended maintenance therapy dose is 400 mcg with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 4, 7, 10, 13, and 19. Patients who achieve a complete response at 25 months and beyond may receive maintenance instillations with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 25, 31, and 37. The maximum treatment duration is 37 months.
The FDA recommends discontinuing treatment if disease persists after second induction or owing to disease recurrence, progression, or unacceptable toxicity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167832</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FC77.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FC77</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240424T091016</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240424T091038</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240424T091038</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240424T091038</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>S Worcester</byline> <bylineText>SHARON WORCESTER, MA</bylineText> <bylineFull>SHARON WORCESTER, MA</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType/> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first-in-class interleukin (IL)-15 superagonist nogapendekin alfa inbakicept-pmln (Anktiva), plus bac</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>The FDA declined an initial approval for the combination in May 2023.</teaser> <title>FDA Approves New Bladder Cancer Drug</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">31</term> </publications> <sections> <term>39313</term> <term canonical="true">27979</term> <term>37225</term> <term>27980</term> </sections> <topics> <term>270</term> <term>278</term> <term canonical="true">214</term> <term>232</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>FDA Approves New Bladder Cancer Drug</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p> <span class="tag metaDescription">The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first-in-class interleukin (IL)-15 superagonist <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://reference.medscape.com/drug/anktiva-nonapendekine-alfa-4000332">nogapendekin alfa</a></span> inbakicept-pmln (Anktiva), plus bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), for the treatment of certain non–muscle-invasive bladder cancers that fail to respond to BCG alone.</span> </p> <p>Specifically, the agent is approved to treat patients with BCG-unresponsive non–muscle-invasive <span class="Hyperlink">bladder cancer</span> carcinoma in situ with or without Ta or T1 papillary disease. <br/><br/>The FDA declined an initial approval for the combination in May 2023 because of deficiencies the agency observed during its prelicense inspection of third-party manufacturing organizations. In October 2023, ImmunityBio resubmitted the Biologics License Application, which <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://immunitybio.com/fda-accepts-immunitybios-bla-resubmission-as-complete-and-sets-new-pdufa-date/">was accepted</a></span>.<br/><br/>The new therapy represents addresses “an unmet need” in this high-risk bladder cancer population, the company stated in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://immunitybio.com/nejm-evidence-publishes-results-for-immunitybios-quilt-3-032-registrational-trial-of-il-15-superagonist-n-803-plus-bcg-in-patients-with-bladder-cancer/">press release</a></span> announcing the initial study findings. Typically, patients with intermediate or high-risk disease undergo bladder tumor resection followed by treatment with BCG, but the cancer recurs in up to 50% of patients, including those who experience a complete response, explained ImmunityBio, which acquired Altor BioScience. <br/><br/>Approval was based on findings from the single arm, phase 2/3 open-label <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03022825">QUILT-3.032 study</a></span>, which included 77 patients with BCG-unresponsive, high-risk disease following transurethral resection. All had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2. <br/><br/>Patients received nogapendekin alfa inbakicept-pmln induction via intravesical instillation with BCG followed by maintenance therapy for up to 37 months. <br/><br/>According to the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-nogapendekin-alfa-inbakicept-pmln-bcg-unresponsive-non-muscle-invasive-bladder-cancer">FDA’s press release</a></span>, 62% of patients had a complete response, defined as a negative <span class="Hyperlink">cystoscopy</span> and urine cytology; 58% of those with a complete response had a duration of response lasting at least 12 months and 40% had a duration of response lasting 24 months or longer.<br/><br/>The safety of the combination was evaluated in a cohort of 88 patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included dysuria, pollakiuria, and <span class="Hyperlink">hematuria</span>, which are associated with intravesical BCG; 86% of these events were grade 1 or 2. Overall, 7% of patients discontinued the combination owing to adverse reactions.<br/><br/>The <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2024/761336s000lbl.pdf">recommended dose</a></span> is 400 mcg administered intravesically with BCG once a week for 6 weeks as induction therapy, with an option for a second induction course if patients don’t achieve a complete response at 3 months. The recommended maintenance therapy dose is 400 mcg with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 4, 7, 10, 13, and 19. Patients who achieve a complete response at 25 months and beyond may receive maintenance instillations with BCG once a week for 3 weeks at months 25, 31, and 37. The maximum treatment duration is 37 months.<br/><br/>The FDA recommends discontinuing treatment if disease persists after second induction or owing to disease recurrence, progression, or unacceptable toxicity. <br/><br/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/fda-approves-new-bladder-cancer-drug-2024a10007t5">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
CRC Screening in Primary Care: The Blood Test Option
Last year, I concluded a commentary for this news organization on colorectal cancer (CRC) screening guidelines by stating that between stool-based tests, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy, “the best screening test is the test that gets done.” But should that maxim apply to the new blood-based screening test, Guardant Health Shield? This proprietary test, which costs $895 and is not generally covered by insurance, identifies alterations in cell-free DNA that are characteristic of CRC.
Shield’s test characteristics were recently evaluated in a prospective study of more than 10,000 adults aged 45-84 at average risk for CRC. The test had an 87.5% sensitivity for stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer but only a 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Test specificity was 89.6%, meaning that about 1 in 10 participants without CRC or advanced precancerous lesions on colonoscopy had a false-positive result.
Although the Shield blood test has a higher rate of false positives than the traditional fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and lower sensitivity and specificity than a multitarget stool DNA (FIT-DNA) test designed to improve on Cologuard, it meets the previously established criteria set forth by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to be covered for Medicare beneficiaries at 3-year intervals, pending FDA approval.
A big concern, however, is that the availability of a blood test may cause patients who would have otherwise been screened with colonoscopy or stool tests to switch to the blood test. A cost-effectiveness analysis found that offering a blood test to patients who decline screening colonoscopy saves additional lives, but at the cost of more than $377,000 per life-year gained. Another study relying on three microsimulation models previously utilized by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found that annual FIT results in more life-years gained at substantially lower cost than blood-based screening every 3 years “even when uptake of blood-based screening was 20 percentage points higher than uptake of FIT.” As a result, a multidisciplinary expert panel concluded that blood-based screening should not substitute for established CRC screening tests, but instead be offered only to patients who decline those tests.
In practice, this will increase the complexity of the CRC screening conversations we have with patients. We will need to be clear that the blood test is not yet endorsed by the USPSTF or any major guideline group and is a second-line test that will miss most precancerous polyps. As with the stool tests, it is essential to emphasize that a positive result must be followed by diagnostic colonoscopy. To addend the cancer screening maxim I mentioned before, the blood test is not the best test for CRC, but it’s probably better than no test at all.
Dr. Lin is a family physician and associate director, Family Medicine Residency Program, Lancaster General Hospital, Lancaster, Pennsylvania. He blogs at Common Sense Family Doctor.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, I concluded a commentary for this news organization on colorectal cancer (CRC) screening guidelines by stating that between stool-based tests, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy, “the best screening test is the test that gets done.” But should that maxim apply to the new blood-based screening test, Guardant Health Shield? This proprietary test, which costs $895 and is not generally covered by insurance, identifies alterations in cell-free DNA that are characteristic of CRC.
Shield’s test characteristics were recently evaluated in a prospective study of more than 10,000 adults aged 45-84 at average risk for CRC. The test had an 87.5% sensitivity for stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer but only a 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Test specificity was 89.6%, meaning that about 1 in 10 participants without CRC or advanced precancerous lesions on colonoscopy had a false-positive result.
Although the Shield blood test has a higher rate of false positives than the traditional fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and lower sensitivity and specificity than a multitarget stool DNA (FIT-DNA) test designed to improve on Cologuard, it meets the previously established criteria set forth by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to be covered for Medicare beneficiaries at 3-year intervals, pending FDA approval.
A big concern, however, is that the availability of a blood test may cause patients who would have otherwise been screened with colonoscopy or stool tests to switch to the blood test. A cost-effectiveness analysis found that offering a blood test to patients who decline screening colonoscopy saves additional lives, but at the cost of more than $377,000 per life-year gained. Another study relying on three microsimulation models previously utilized by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found that annual FIT results in more life-years gained at substantially lower cost than blood-based screening every 3 years “even when uptake of blood-based screening was 20 percentage points higher than uptake of FIT.” As a result, a multidisciplinary expert panel concluded that blood-based screening should not substitute for established CRC screening tests, but instead be offered only to patients who decline those tests.
In practice, this will increase the complexity of the CRC screening conversations we have with patients. We will need to be clear that the blood test is not yet endorsed by the USPSTF or any major guideline group and is a second-line test that will miss most precancerous polyps. As with the stool tests, it is essential to emphasize that a positive result must be followed by diagnostic colonoscopy. To addend the cancer screening maxim I mentioned before, the blood test is not the best test for CRC, but it’s probably better than no test at all.
Dr. Lin is a family physician and associate director, Family Medicine Residency Program, Lancaster General Hospital, Lancaster, Pennsylvania. He blogs at Common Sense Family Doctor.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, I concluded a commentary for this news organization on colorectal cancer (CRC) screening guidelines by stating that between stool-based tests, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy, “the best screening test is the test that gets done.” But should that maxim apply to the new blood-based screening test, Guardant Health Shield? This proprietary test, which costs $895 and is not generally covered by insurance, identifies alterations in cell-free DNA that are characteristic of CRC.
Shield’s test characteristics were recently evaluated in a prospective study of more than 10,000 adults aged 45-84 at average risk for CRC. The test had an 87.5% sensitivity for stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer but only a 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Test specificity was 89.6%, meaning that about 1 in 10 participants without CRC or advanced precancerous lesions on colonoscopy had a false-positive result.
Although the Shield blood test has a higher rate of false positives than the traditional fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and lower sensitivity and specificity than a multitarget stool DNA (FIT-DNA) test designed to improve on Cologuard, it meets the previously established criteria set forth by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to be covered for Medicare beneficiaries at 3-year intervals, pending FDA approval.
A big concern, however, is that the availability of a blood test may cause patients who would have otherwise been screened with colonoscopy or stool tests to switch to the blood test. A cost-effectiveness analysis found that offering a blood test to patients who decline screening colonoscopy saves additional lives, but at the cost of more than $377,000 per life-year gained. Another study relying on three microsimulation models previously utilized by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found that annual FIT results in more life-years gained at substantially lower cost than blood-based screening every 3 years “even when uptake of blood-based screening was 20 percentage points higher than uptake of FIT.” As a result, a multidisciplinary expert panel concluded that blood-based screening should not substitute for established CRC screening tests, but instead be offered only to patients who decline those tests.
In practice, this will increase the complexity of the CRC screening conversations we have with patients. We will need to be clear that the blood test is not yet endorsed by the USPSTF or any major guideline group and is a second-line test that will miss most precancerous polyps. As with the stool tests, it is essential to emphasize that a positive result must be followed by diagnostic colonoscopy. To addend the cancer screening maxim I mentioned before, the blood test is not the best test for CRC, but it’s probably better than no test at all.
Dr. Lin is a family physician and associate director, Family Medicine Residency Program, Lancaster General Hospital, Lancaster, Pennsylvania. He blogs at Common Sense Family Doctor.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167815</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FBDD.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FBDD</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>353</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240423T115627</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240423T125432</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240423T125432</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240423T125432</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Kenneth W. Lin, MD</byline> <bylineText>KENNETH W. LIN, MD, MPH</bylineText> <bylineFull>KENNETH W. LIN, MD, MPH</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>Opinion</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>If public and private payers start covering Shield alongside other CRC screening tests, it presents an opportunity for primary care physicians to reach the appr</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <title>CRC Screening in Primary Care: The Blood Test Option</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>GIHOLD</publicationCode> <pubIssueName>January 2014</pubIssueName> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">31</term> <term>21</term> <term>15</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">52</term> <term>41022</term> </sections> <topics> <term>67020</term> <term canonical="true">280</term> <term>270</term> <term>278</term> <term>263</term> <term>213</term> <term>38029</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>CRC Screening in Primary Care: The Blood Test Option</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Last year, I concluded a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/995196">commentary</a></span> for this news organization on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2500006-overview">colorectal cancer</a></span> (CRC) screening guidelines by stating that between stool-based tests, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1637664-overview">flexible sigmoidoscopy</a></span>, and <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1819350-overview">colonoscopy</a></span>, “the best screening test is the test that gets done.” But should that maxim apply to the new blood-based screening test, Guardant Health Shield? This proprietary test, which costs $895 and is not generally covered by insurance, <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2023/0600/diagnostic-tests-guardant-health-shield-colon-cancer.html">identifies alterations in cell-free DNA that are characteristic of CRC</a></span>.</p> <p>Shield’s test characteristics were recently evaluated in a <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMe2311101">prospective study</a></span> of more than 10,000 adults aged 45-84 at average risk for CRC. The test had an 87.5% sensitivity for stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer but only a 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Test specificity was 89.6%, meaning that about 1 in 10 participants without CRC or advanced precancerous lesions on colonoscopy had a false-positive result.<br/><br/>Although the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2310336?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed">Shield blood test</a></span> has a higher rate of false positives than the traditional fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and lower sensitivity and specificity than a multitarget stool DNA (FIT-DNA) test designed to improve on Cologuard, it meets the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.cms.gov/files/document/mm12280.pdf">previously established criteria</a></span> set forth by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to be covered for Medicare beneficiaries at 3-year intervals, pending FDA approval.<span class="tag metaDescription"> If public and private payers start covering Shield alongside other CRC screening tests, it presents an opportunity for primary care physicians to reach the approximately <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2023/pdf/23_0071.pdf">3 in 10 adults between ages 45 and 75 who are not being routinely screened</a></span>.</span><br/><br/>A big concern, however, is that the availability of a blood test may cause patients who would have otherwise been screened with colonoscopy or stool tests to switch to the blood test. A <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2811942">cost-effectiveness analysis</a></span> found that offering a blood test to patients who decline screening colonoscopy saves additional lives, but at the cost of more than $377,000 per life-year gained. <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(24)00174-4/fulltext?referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fpubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2F">Another study</a></span> relying on three microsimulation models previously utilized by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found that annual FIT results in more life-years gained at substantially lower cost than blood-based screening every 3 years “even when uptake of blood-based screening was 20 percentage points higher than uptake of FIT.” As a result, a multidisciplinary <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.cghjournal.org/article/S1542-3565(24)00162-9/abstract">expert panel concluded</a></span> that blood-based screening should not substitute for established CRC screening tests, but instead be offered only to patients who decline those tests.<br/><br/>In practice, this will increase the complexity of the CRC screening conversations we have with patients. We will need to be clear that the blood test is not yet endorsed by the USPSTF or any major guideline group and is a second-line test that will miss most precancerous polyps. As with the stool tests, it is essential to emphasize that a positive result must be followed by diagnostic colonoscopy. To addend the cancer screening maxim I mentioned before, the blood test is not the best test for CRC, but it’s probably better than no test at all.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>Dr. Lin is a family physician and associate director, Family Medicine Residency Program, Lancaster General Hospital, Lancaster, Pennsylvania. He blogs at <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://commonsensemd.blogspot.com/">Common Sense Family Doctor.</a></span></em> </p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/crc-screening-primary-care-blood-test-option-2024a10007gf">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>“The best screening test is the test that gets done,” but should that maxim apply to the new blood-based screening test?</p> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
Weighing the Benefits of Integrating AI-based Clinical Notes Into Your Practice
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167723</fileName> <TBEID>0C04F96F.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04F96F</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>353</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240422T171622</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240422T173902</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240422T173902</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240422T173902</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD</byline> <bylineText>ARTURO LOAIZA-BONILLA, MD</bylineText> <bylineFull>ARTURO LOAIZA-BONILLA, MD</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>Opinion</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided atte</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>Artificial intelligence expert Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, discusses the benefits of AI-based clinical notes.</teaser> <title>Weighing the Benefits of Integrating AI-based Clinical Notes Into Your Practice</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdid</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">31</term> <term>26</term> <term>25</term> <term>23</term> <term>22</term> <term>52226</term> <term>58877</term> <term>51892</term> <term>21</term> <term>18</term> <term>15</term> <term>13</term> <term>9</term> <term>34</term> <term>6</term> <term>5</term> </publications> <sections> <term>41022</term> <term canonical="true">52</term> </sections> <topics> <term>278</term> <term canonical="true">38029</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>Weighing the Benefits of Integrating AI-based Clinical Notes Into Your Practice</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. <a href="https://twitter.com/StuartBlitz/status/1754302729109795224?s=20">In a recent X post</a>, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?” </p> <p>This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.<br/><br/>The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation</h2> <p>The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.</p> <p>How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:<br/><br/><b>Data capture and processing:</b> ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.<br/><br/><span class="Strong">Natural language processing (NLP):</span> A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.<br/><br/><span class="Strong">Deep learning:</span> Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.<br/><br/><span class="Strong">Integration with electronic health records (EHRs):</span> ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.<br/><br/><span class="Strong">Customization and personalization:</span> Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.<br/><br/><span class="Strong">Ethical and privacy considerations:</span> ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation</h2> <ul class="body"> <li><b>Reducing clinician burnout:</b> By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.</li> <li><b>Enhanced patient care:</b> With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.</li> <li><b>Data accuracy and quality:</b> AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.</li> <li><b>Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare:</b> AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.</li> </ul> <p>The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.<br/><br/>In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with <a href="https://www.nuance.com/healthcare/dragon-ai-clinical-solutions/dax-copilot.html">DAX</a> as an example.<br/><br/>I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at <a href="mailto:Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com">Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com</a> or find me on X <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://twitter.com/@DrBonillaOnc">@DrBonillaOnc</a></span>.<span class="end"/></p> <p> <em>Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.</em> </p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/weighing-benefits-integrating-ai-based-clinical-notes-your-2024a10006r5">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>
New Federal Rule Delivers Workplace Support, Time Off for Pregnant Docs
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
<!--$RCSfile: InCopy_agile.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.35 $-->
<!--$RCSfile: drupal.xsl,v $ $Revision: 1.7 $-->
<root generator="drupal.xsl" gversion="1.7"> <header> <fileName>167809</fileName> <TBEID>0C04FBCA.SIG</TBEID> <TBUniqueIdentifier>MD_0C04FBCA</TBUniqueIdentifier> <newsOrJournal>News</newsOrJournal> <publisherName>Frontline Medical Communications</publisherName> <storyname/> <articleType>2</articleType> <TBLocation>QC Done-All Pubs</TBLocation> <QCDate>20240422T165833</QCDate> <firstPublished>20240422T165844</firstPublished> <LastPublished>20240422T165844</LastPublished> <pubStatus qcode="stat:"/> <embargoDate/> <killDate/> <CMSDate>20240422T165844</CMSDate> <articleSource/> <facebookInfo/> <meetingNumber/> <byline>Steph Weber</byline> <bylineText>STEPH WEBER</bylineText> <bylineFull>STEPH WEBER</bylineFull> <bylineTitleText/> <USOrGlobal/> <wireDocType/> <newsDocType>News</newsDocType> <journalDocType/> <linkLabel/> <pageRange/> <citation/> <quizID/> <indexIssueDate/> <itemClass qcode="ninat:text"/> <provider qcode="provider:imng"> <name>IMNG Medical Media</name> <rightsInfo> <copyrightHolder> <name>Frontline Medical News</name> </copyrightHolder> <copyrightNotice>Copyright (c) 2015 Frontline Medical News, a Frontline Medical Communications Inc. company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, copied, or otherwise reproduced or distributed without the prior written permission of Frontline Medical Communications Inc.</copyrightNotice> </rightsInfo> </provider> <abstract/> <metaDescription>Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Oppor</metaDescription> <articlePDF/> <teaserImage/> <teaser>Newly updated guidelines for the federal Pregnant Workers Fairness Act could help physicians better balance career and family.</teaser> <title>New Federal Rule Delivers Workplace Support, Time Off for Pregnant Docs</title> <deck/> <disclaimer/> <AuthorList/> <articleURL/> <doi/> <pubMedID/> <publishXMLStatus/> <publishXMLVersion>1</publishXMLVersion> <useEISSN>0</useEISSN> <urgency/> <pubPubdateYear/> <pubPubdateMonth/> <pubPubdateDay/> <pubVolume/> <pubNumber/> <wireChannels/> <primaryCMSID/> <CMSIDs/> <keywords/> <seeAlsos/> <publications_g> <publicationData> <publicationCode>im</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>rn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>pn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>oncr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>ob</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>nr</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalTitle> <journalFullTitle>Neurology Reviews</journalFullTitle> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdsurg</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement>2018 Frontline Medical Communications Inc.,</copyrightStatement> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdemed</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>mdid</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>hemn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>fp</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>skin</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>cpn</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>endo</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>chph</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>card</publicationCode> <pubIssueName/> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> </publicationData> <publicationData> <publicationCode>GIHOLD</publicationCode> <pubIssueName>January 2014</pubIssueName> <pubArticleType/> <pubTopics/> <pubCategories/> <pubSections/> <journalTitle/> <journalFullTitle/> <copyrightStatement/> </publicationData> </publications_g> <publications> <term canonical="true">21</term> <term>26</term> <term>25</term> <term>31</term> <term>23</term> <term>22</term> <term>52226</term> <term>58877</term> <term>51892</term> <term>18</term> <term>15</term> <term>13</term> <term>9</term> <term>34</term> <term>6</term> <term>5</term> </publications> <sections> <term canonical="true">27980</term> <term>39313</term> </sections> <topics> <term>322</term> <term canonical="true">38029</term> <term>50194</term> <term>278</term> </topics> <links/> </header> <itemSet> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>Main</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title>New Federal Rule Delivers Workplace Support, Time Off for Pregnant Docs</title> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> <p>Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum. </p> <p>The <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.eeoc.gov/newsroom/eeoc-issues-final-regulation-pregnant-workers-fairness-act">Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA)</a></span> aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/restricted-abortion-access-tied-mental-health-harm-2024a10001u9">mental conditions</a></span> associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”<br/><br/>Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship. <br/><br/>Female doctors have historically encountered <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/987608">significant barriers</a></span> to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of <span class="Hyperlink">infertility</span>, <span class="Hyperlink">miscarriage</span>, and pregnancy complications than in the general population. <br/><br/>Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0022480423000987">at risk</a></span>, with 42% reporting at least one <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://reference.medscape.com/article/266317-overview">pregnancy loss</a></span>. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations. <br/><br/>Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career. <br/><br/>She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”<br/><br/>Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014. <br/><br/>Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”<br/><br/>After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.regulations.gov/document/EEOC-2023-0004-0001">nearly 100,000 comments</a></span>, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause. <br/><br/>The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.federalregister.gov/public-inspection/2024-07527/implementation-of-the-pregnant-workers-fairness-act">unpublished version</a></span> of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.<br/><br/></p> <h2>Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms</h2> <p>The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/979276">breastfeeding employees</a></span> and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.</p> <p>FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks. <br/><br/>Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said. <br/><br/>Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.abms.org/newsroom/abms-member-boards-leave-policies-help-residents-care-for-their-own-families/">requiring its member boards</a></span> with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery. <br/><br/>Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive <span class="Hyperlink">6 weeks of paid leave</span>. <br/><br/>“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments. <br/><br/>This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her <span class="Hyperlink">cesarean delivery</span>. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6. <br/><br/>“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jaccas.2019.05.028">survey</a></span> in the <em>Journal of the American College of Cardiology</em> called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors. <br/><br/>Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause. <br/><br/>“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein. <br/><br/></p> <p> <em>A version of this article appeared on <span class="Hyperlink"><a href="https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/new-federal-rule-delivers-workplace-support-time-pregnant-2024a10007k1">Medscape.com</a></span>.</em> </p> </itemContent> </newsItem> <newsItem> <itemMeta> <itemRole>teaser</itemRole> <itemClass>text</itemClass> <title/> <deck/> </itemMeta> <itemContent> </itemContent> </newsItem> </itemSet></root>

